- PAST QUESTION PAPERS
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2017 Question Paper
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2018 Question Paper
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2019 Question Paper
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2021 Question Paper
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2022 Question Paper
- Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2023 Question Paper
- SOLVED ANSWERS
- Practice Questions
Are you a instructor or student of Bachelor in Hotel Management (BHM) at Tribhuvan University? Looking for previous years’ question papers for the 5th semester subject “Hospitality Marketing and Sales”? You’ve come to the right place! This post provides a comprehensive collection of question papers from past years to help you prepare effectively for your exams.
How to Use These Question Papers
- Start Early: Begin practicing with these question papers well in advance of your exam.
- Create a Study Plan: Allocate specific times for each topic and stick to your schedule.
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Attempt these papers in a timed setting to get used to the pressure of the actual exam.
- Review Your Answers: After solving the papers, compare your answers with standard solutions or discuss with peers to identify areas of improvement.
PAST QUESTION PAPERS
| Dear Students, If you find any question paper missing from any year, please contact us through our email address “bhmaims@gmail.com“ Also, if you have any missing past-year board question papers, kindly forward them to us so that we can update in our website. |
Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2017 Question Paper

Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2018 Question Paper

Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2019 Question Paper

Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2021 Question Paper

Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2022 Question Paper

Hospitality Marketing and Sales Year 2023 Question Paper

Preparing for your BHM 5th semester exams in “Hospitality Marketing and Sales” can be difficult and challenging, but with the right resources and a solid study plan, you can do it very easily. Make the most of these previous years’ question papers to boost your confidence and performance. Good luck!
SOLVED ANSWERS
Solved Answers of Year 2017
- Clarify the term marketing environment. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ The marketing environment refers to the external and internal factors that influence a company’s marketing activities, including its ability to serve customers, adapt to market changes, and compete. It consists of the microenvironment (customers, suppliers, competitors) and the macroenvironment (economic, political, technological, cultural factors). - What is intensive distribution in food and service? (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Intensive distribution is a marketing distribution strategy which is used to distribute or supply products and services in as many outlets as possible to maximize availability and consumer access. This approach is commonly applied in the food and service industries where high-demand, everyday products need to be readily accessible to a wide range of consumers.
Intensive distribution ensures that products like snacks, beverages, or packaged foods are available in numerous retail outlets. For example: KFC, Pepe Pizza, Domino’s, Starbucks, etc. - Define strategic planning. (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
→ Strategic planning can be defined as the process of defining an organization’s long-term goals and determining the best strategies and actions to achieve them within a certain time period. It involves evaluating the current situation, setting a achievable objectives, and developing a roadmap to support decision-making and resource allocation to ensure long-term success and competitiveness. - What is branding of a hospitality product? (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Branding of a hospitality product refers to the process of creating a unique identity, image, and reputation for a hotel, restaurant, resort, or other hospitality services in the minds of consumers.
It involves developing a unique set of values, experiences, and promises that differentiate the hospitality service from competitors and build emotional connections with customers.
For example: Soaltee Hotel as Brand, Siddharta Hospitality Group, Bajeko Sekuwa, etc. - Define franchising in food and service. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Franchising in food and service refers to a business model where a company (the franchisor) grants a license to an individual or entity (the franchisee) to operate a business using the franchisor’s brand, systems, and products. In return, the franchisee pays an initial franchise fee and ongoing royalties to the franchisor. - Clarify the term competitive advantage. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Competitive advantage refers to a company’s ability to outperform its competitors by offering greater value to its customers, either through lower prices, superior quality, unique products, or better customer service. It is the advantage that sets a company apart in the market, allowing it to attract more customers, gain higher market share, or generate more profit compared to its competitors. - What is interactive marketing? (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Interactive marketing refers to a marketing strategy that involves a two-way communication process between the business and its customers which is designed to engage customers in real-time, - Define the term outgoing calls. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Outgoing calls are phone calls initiated by a salesperson or service representative to reach out to customers or prospects for various purposes, such as selling or promoting products and services, providing information, or following up on inquiries, gathering feedback and reviews, etc. - Write short notes on perceptual mapping? (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Perceptual mapping is a visual representation used in marketing to display the positioning of different brands, products, or services in the minds of consumers. - What is a syndicated research? (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Syndicated research is a type of market research conducted and funded by a research firm, but the results are made available to multiple clients or organizations.
Rather than being commissioned by a single company for a specific need, syndicated research is carried out independently by the research firm, which then sells the data and findings to various interested parties. - What is marketing research? Write its importance. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
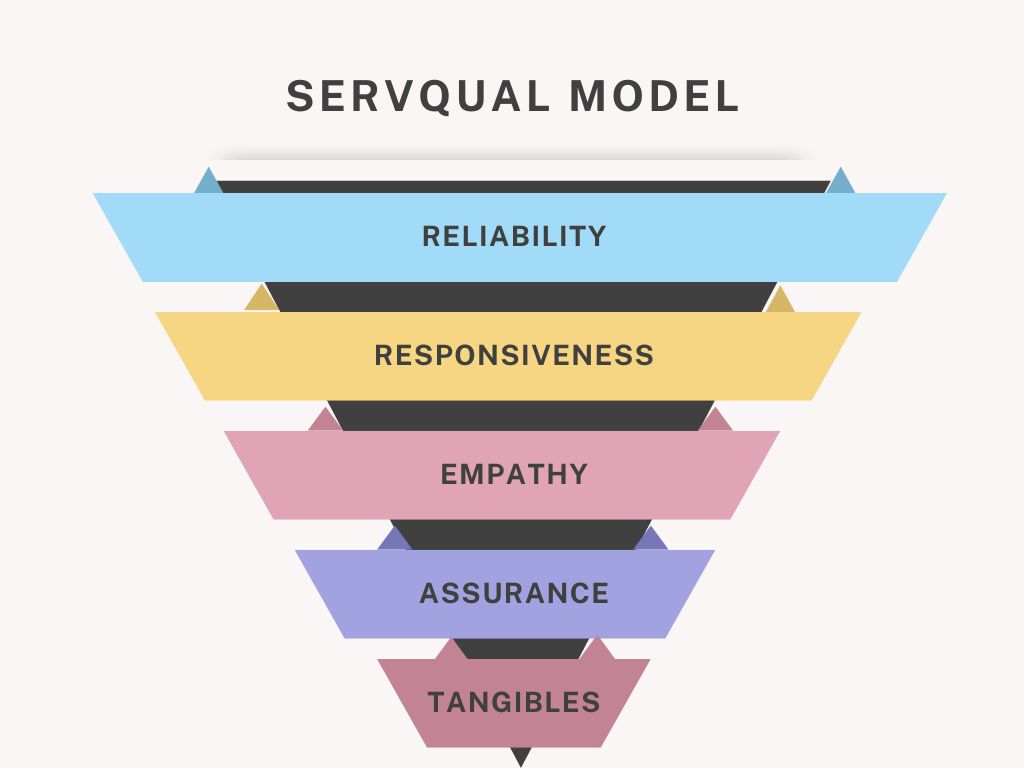
→ Repeated question from Year 2022 Question 18 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Briefly explain some dimensions of service quality. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ The SERVQUAL model is a widely used tool developed by Parasuraman, Zeithaml, and Berry for measuring service quality by evaluating the gap between customer expectations and perceptions of the actual service delivered. This model helps businesses identify areas for improvement to enhance customer satisfaction. It is based on five dimensions of service quality:- Tangibility: The physical aspects of the service, such as the appearance of facilities, staff uniforms, and cleanliness, which provide visual cues about the quality of the service.
- Reliability: The ability to consistently deliver the promised service accurately and dependably, such as honoring reservations or ensuring timely room service.
- Responsiveness: The willingness and ability of staff to assist customers and provide prompt service, such as quickly addressing guest requests or complaints.
- Assurance: The knowledge and courtesy of employees, and their ability to inspire trust and confidence in the service, ensuring guests feel secure in the quality and safety of the service provided.
- Empathy: The personalized attention and care provided to customers, such as tailoring services to meet individual guest preferences and making them feel valued.
- Define the term market segmentation and why are the different factors to be determine the market segmentation? (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into smaller, more defined categories based on shared characteristics.
The factors to be determined to be determined the market segmentation are:- Geographic Segmentation: Dividing the market based on geographic locations, such as countries, regions, cities, or neighborhoods.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Involves segmenting the market based on consumer behavior, including purchase habits, brand loyalty, usage rates, and responses to marketing messages.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Focuses on consumers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and personality traits.
- Technological Segmentation: Categorizes consumers based on their technology usage and familiarity with digital platforms.
- Demographic Segmentation: Involves categorizing the market based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, and family size.
- What do you understand by hospitality marketing environment? Write about the macro and micro environment. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Hospitality marketing environment can be defined as all those internal and external forces or set of conditions, events and influences which directly or indirectly influence the organizations decisions and actions.
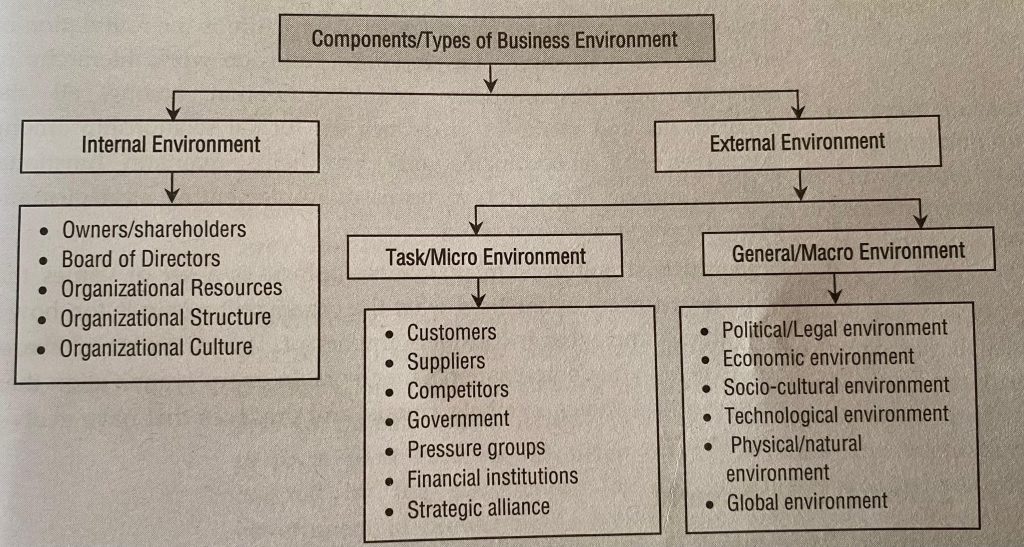
Micro- Environment:
Micro-environment are also called specific environment or task environment. They are such environment which have direct and immediate impact on managerial decisions and actions and are also directly relevant to the achievement of organizational goals.
Micro-environment include COSMIC i.e.
C – Competitors
O – Organization
S – Suppliers
M – Media
I – Intermediaries
C – Customers
- Competitors: Competition is a basic features of an open market economy. Competitors are rivals that compete with the organization for resources. No business can ignore its competitors and their business strategy. Therefore, a manager of an organization should have ability to forecast customers’ demand and develop new strategies to increase market share.
- Organization: Organization encompasses employee, management, rules and regulations, organization structure, internal communication, organizational goals, etc.
- Suppliers: Suppliers are parties and institutions that supply materials, machines and other resources to organizations. The management of every organization seeks to ensure regular and steady flow of needed inputs at a reasonable price. However, if suppliers do not supply materials in time and also charge high price, it reduces organizational effectiveness.
- Media: Media falls under ‘Pressure group’. Pressure groups are special interest groups, which may also create problems and difficulties in business activities. They exert considerable influence by using the media of Labour unions affiliated with political parties, consumers associations, humans rights activists, environmental associations, media, social institutions, etc.
Media encompasses various channels and platforms which are used to communicate information and promotional content to the public, including traditional media (TV, radio, print) and digital media (social media, blogs, websites). - Intermediaries: Intermediaries are a key component of the micro business environment in the hospitality industry. They play a vital role in connecting businesses with customers, enhancing distribution efficiency, and facilitating marketing and promotion. While they offer significant benefits, such as increased market reach and cost savings, businesses must also manage the challenges associated with dependency and commission costs. Effective collaboration with intermediaries can lead to better market penetration and improved customer service.
- Customers: Customers pay money for goods and services and are main source of revenue. They represent potential uncertainty to an organization because their tastes and preferences may change with the change in time and fashion. New products and services, new methods of marketing, and more discriminating customers have all added uncertainty to organizations.
A satisfied customer today might not be same tomorrow. Therefore, it is necessary to collect information about preferences and demands of customers through market research, survey and rport form representatives and other means.
Macro Environment
It is also known as General Environment’ or ‘Remote Environment’. They are broad external conditions that may affect the business activities of an organization. It is uncontrollable and require proper monitoring of the components to adapt on the basis of emerging changes. It creates both opportunities and threats to the business organizations.
It includes PESTEL i.e.
P – Political environment
E – Environmental environment
S – Socio-Cultural environment
T – Technological environment
E – Economic environment
L – Legal environment
- Political Environment: These refers to government regulations and the legal system for business. It involves constitutions, political philosophy, political systems, political parties, political institutions and pressure groups.
Usually, political institution is the influence of three institutions – judiciary, legislature, and executive which plays major roles in directing, developing and controlling business activities. - Environmental Environment: This incorporates natural and artificial infrastructures and facilities that provide opportunities for social and business activities and development. The components includes lands, water supply, plants and animals, buildings and other infrastructures. It also involves all vegetation, micro-organisms, soil rock, climate and other natural resources along with environmental laws and policies.
- Socio-Cultural Environment: The socio-cultural environment is comprehensive since it includes the total social forces within which an organization operate. It involves tradition, social values, beliefs, norms, attitudes, customs and demographic composition of nation. All the elements of socio-culture environment are adaptable, shared and inter-related.
Socio-culture environment determines the products, services and standards of conduct that the society is likely to value. The common elements of socio-cultural environment are: demography, age groups, size and distribution of population, gender ratio, urbanization, migration of people, ethnicity, lifestyle, social values, religion, language, attitude, value and belief, etc. - Economic Environment: It includes all factors which give shape and form to economic activities. Those factors consist of interest rates, per-capita income, GDP, GNI, inflation, change in disposable income, stock market fluctuation and stage of general business cycle. These factors affect demand of products and services in the market.
There is close relationship between business and general economic environment. Business organizations gets inputs from economic environment and they also supply their outputs to economic environment. - Legal Environment: Legal environment involves laws, rules, and regulations enacted by legislation and government for systematization of administrative and business activities of a country. It plays a dominating role over the decision of public and private enterprises. Legal environment involves the code of conduct that defines legal boundaries for all the activities of the country including business.
- What is distribution in hospitality marketing? Highlight the distribution channels of hospitality products. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Distribution in hospitality marketing refers to the process of delivering hospitality products or services from hospitality organizations to final customer.
The distribution channels of hospitality products are:- Travel Agents
- Tour Wholesaler
- Global Distribution Channels (GDS)
- Home Delivery (Take out and Delivery Service)
- Franchise Systems
- What are the nature of hospitality product and services? Discuss. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ The nature of hospitality product and services are:- Inseparability: In the hospitality industry, services are produced and consumed at the same time. The service provider and the customer must both be present for the service to occur.
- Intangibility: Hospitality services are intangible, meaning they cannot be touched, stored, or owned. Customers experience services through their perceptions, feelings, and satisfaction.
For example: When a guest order MoMo in hotel, along with tangible food and beverages, food service also provide an intangible services like convenience, hospitality, social contact, atmosphere, relaxation and sometimes entertainment also. - Perishability: Hospitality services cannot be stored for future use. Once the opportunity to sell the service is gone, the revenue is lost forever.
- Variability (Heterogeneity): The quality of services in hospitality can vary widely depending on who delivers the service, when, and where. No two experiences are exactly the same.
- Labor Intensive: The hospitality industry heavily relies on human labor to deliver services, making staff a critical component of the service experience.
- Absence of Ownership: In hospitality, customers pay for the right to use or experience a service but do not take ownership of any tangible product.
Example: When a guest stays at a hotel, they are paying for the use of the room for a specific period, but they do not own the room or any of the hotel’s facilities. When a guest stays at a hotel, they are paying for the use of the room for a specific period, but they do not own the room or any of the hotel’s facilities.
This absence of ownership makes the focus on the overall experience and customer satisfaction more important. Since customers do not take anything physical away from the transaction, their judgment is based on how well their needs were met during the service encounter. - People as part of product: The interaction between staff and customers is a fundamental part of the hospitality service. The service is often delivered by people, and how they perform directly impacts customer satisfaction. Due to this, maintaining a quality control is very difficult in service industry.
For example: A guest’s experience at a restaurant or hotel is influenced not only by the physical environment but also by how the staff treats them, including their friendliness, attentiveness, and professionalism. - Fluctuating demand patterns: Demand for hospitality services often fluctuates due to factors such as seasonality, holidays, economic conditions, and customer preferences.
- Different channels of distribution: In other packaged products, channels of distribution includes brokers, wholesalers, retailers and other intermediaries. But in hospitality service, general channels of distribution includes travel agents, tour wholesalers, Global Distribution System (GDS), Home delivery services (take-out and delivery service), franchise system, etc.
- Before starting any hospitality business it is necessary to analyze the SWOT concept. Why? Explain SWOT analysis and its importance in the formulation of tourism and hospitality marketing strategy. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ SWOT analysis is the study of strength, weakness, opportunity and threat that an organization has to capitalize and face in operating a business or project. SWOT analysis is the primary stage of strategic planning and concentrates on collecting information from the environment.
The importance of SWOT analysis in the formulation of tourism and hospitality marketing strategy are:- Strategic Planning: Provides a clear understanding of internal and external factors to supports marketing strategies with business goals.
- Market Positioning: Helps define a unique value proposition and differentiate the business from competitors.
- Resource Allocation: Guides efficient allocation of resources to areas with the highest potential for growth and improvement.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential threats and supports the development of contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
- Opportunity Exploitation: Enables businesses to capitalize on emerging trends and expand market reach.
- Competitive Analysis: Provides insights into competitive advantages and areas for improvement compared to competitors.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Ensures informed decisions by offering a comprehensive view of internal and external factors impacting the business
- Effective marketing plan always help to meet the target and to achieve the goal set by the management. What do you understand by market plan? Write the different steps involves in preparing strategic plan of any hospitality organization. (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
→
Solved Answers of Year 2018
- Define the term “special service”. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ The term “special service” refers to any additional or customized service offered by a business, beyond the standard offerings, to meet specific customer needs or enhance their experience and satisfactions and also to exceed their expectations. - List out the major properties that must be prepared for sales presentation. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ The major properties that must be prepared for sales preparation are:- Depth Product or Service Knowledge
- Target audience information like their needs, wants, pain points, etc.
- Competitive knowledge: Knowledge of how your product or service is unique or different or better from competitor
- Well structed sales pitch
- Visual aids like audios, videos, brochures, flyers, etc.
- Customer testimonials
- Pricing details along with offers, discounts or other forms of promotions
- Define the term incoming calls. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Special services are unique customized, premium offerings provided by businesses to enhance customer experiences or satisfaction by catering to unique needs, preferences, or occasions, often going beyond standard service levels to provide added value and exclusivity. - Point out the major types of traveler. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ The major types of traveler are:- Leisure
- Family
- Adventure
- Cultural
- Medical
- Pilgrimage
- Solo
- Group
- Define the term intermediaries. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Intermediaries are entities or individuals that act as the middle link between producers or service providers and consumers, facilitating the flow of goods, services, and information between the two.
Common intermediaries in hospitality industry include travel agents, online travel agencies (OTAs), tour operators, Global Distribution System (GDS) and event planners & conference organizers. - Highlight the major objectives of sales force. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ The major objectives of sales force are:- to increase the company sales
- to attract new customers to expand the business.
- to maintain a very strong relationships with existing customers for repeat business.
- to promote, introduce and sell new products or services to customers
- to represent the company and enhance brand image or market reputation
- to gather valuable data about competitors, customers needs and new market trends
- Define the term positioning strategy. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Positioning strategy refers to the process of establishing a brand or product’s unique place in the minds of consumers relative to competitors. It involves defining how a brand wants to be perceived in the market and what differentiates it from others. - What do you mean by service quality and satisfaction? (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Service quality refers to the overall evaluation or measure of how well a service meets or exceeds customer expectations. It is a critical factor in the hospitality industry, where customers evaluate the intangible aspects of the service they receive, such as responsiveness, reliability, and empathy from staff, along with tangible elements like cleanliness and ambiance.
Customer satisfaction is the result of the customer’s perception of the service quality and their overall experience which reflects the degree to which a service has fulfilled or surpassed the customer’s expectations. If service quality matches or exceeds expectations, the customer is likely to be satisfied. However, if the service falls short, the customer may be dissatisfied. - What is syndicate research? (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Repeated question from 2017 Question Number 10 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - List out the five major types of accommodation.
→ The major fives types of accommodation are:- Hotels
- Resorts
- Motels
- Inns
- Villas
- Homestays
- Camping and Glamping sites (Campsites)
- Apartments
- Guest house
- Cottages
- What is perspective mapping? Explain with diagram. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Perspective mapping is a visual tool that shows and analyzes the different viewpoints and experiences of different stakeholder or employees regarding a specific issue, product, or service, helping organizations to understand relationships and identify areas for improvement.
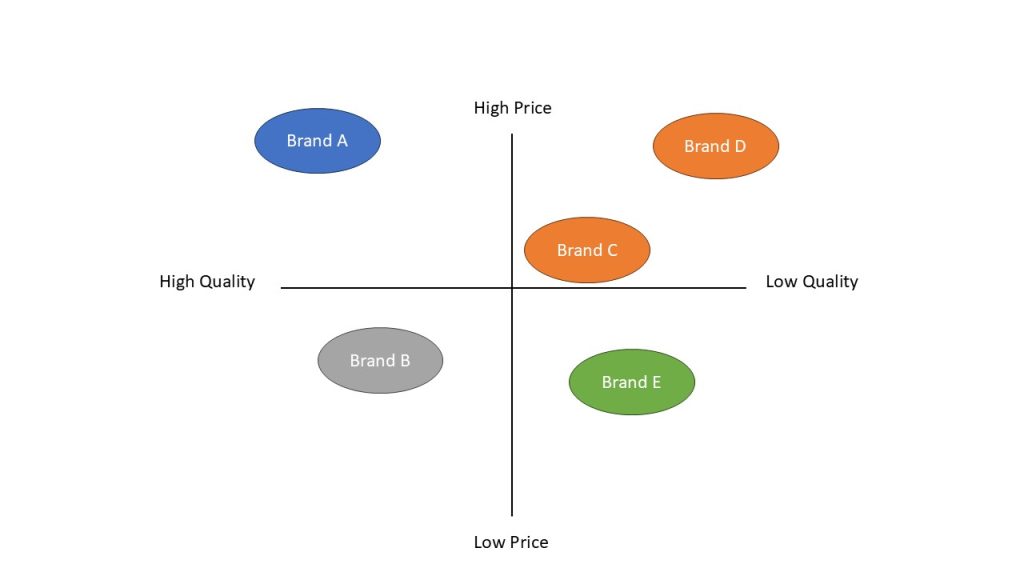
- What is organizational buying? Highlight and explain its steps. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Organizational buying can be defined as the structured, formal and complex decision making process by which organizations or firms, such as businesses, governments, or institutions, purchase goods or services to fulfill their operational, production, or resale needs.
The steps of organizational buying are:- General Need Description: Defines the general characteristics of the required item.
- Product Specification: Details the specific technical requirements.
- Supplier Search: Looks for suppliers that can meet the needs.
- Proposal Solicitation: Invites suppliers to submit bids or proposals.
- Supplier Selection: Evaluates and selects the best supplier.
- Order-Routine Specification: Finalizes purchase terms and conditions.
- Performance Review: Assesses the supplier and product performance post-purchase.
- What is internal marketing? Highlight its benefits. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Internal marketing refers to the practice of treating employees as internal customers, ensuring they are informed, engaged, and motivated to provide excellent service and align with the company’s objectives.
It focuses on promoting the company’s values, goals, and products to employees, encouraging them to contribute to the organization’s success. Internal marketing is more important when the employees are in direct contact with customers or clients because employee themselves became a part of a product and only happy employee can provide a better service to make happy customer.
The benefits of internal marketing are as follow:- Improved Employee Engagement: Motivated and informed employees feel valued, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and commitment.
- Better Customer Service: Employees who understand and believe in the company’s mission are more likely to provide excellent service to external customers.
- Increased Productivity: Engaged employees tend to be more productive, as they are aligned with the company’s goals and objectives.
- Stronger Teamwork: Internal marketing fosters collaboration and communication, creating a positive work culture.
- Lower Turnover Rates: By focusing on employee satisfaction, companies can reduce turnover and retain top talent.
- Brand Advocacy: Employees become brand ambassadors, promoting the company positively both internally and externally.
- What is market segmentation? Define its considerable factors in segmentation program. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from 2017 Question Number 13 (Please refer back to that year) - What is market positioning? Define its major strategy. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Market positioning is process of creating a distinct or unique mental image or position of any product or services in the customers mind as compared to other brands in the market.
The major strategies of positional marketing are:- Pricing-based strategies: focuses on offering best value for price or being most affordable option in the market
It tries to attract cost-conscious customers by offering lower price compared to other competitors. Its main features are discounts, sales, affordable, or cost leadership. - Quality-based strategies: Focuses on providing high quality products or services, regardless of price
Its main objective is to attract those customers who prioritize quality over cost. - Product or differentiation-based strategies
- Convenience-based strategies
- Characteristic-based strategies
- Customer service
- User group
- Pricing-based strategies: focuses on offering best value for price or being most affordable option in the market
- What is distribution? Highlight the distribution channels of tangible and hospitality goods in chart. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Repeated question from 2017 Question Number 15 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Product differentiation is a major tool, which can help and organization be successful in the competitive market. Describe what you know about its meaning and write about its importance explaining its types. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Product differentiation is a marketing strategy where a company makes its product or service stand out from competitors by emphasizing its unique features, quality, or value. The goal is to highlight aspects that make the product distinct and more appealing to the target market, leading to a competitive edge.
The importance of product differentiation are:- Competitive Advantage: Differentiation allows businesses to distinguish themselves in a crowded market, giving them an edge over competitors.
- Customer Loyalty: Unique products attract and retain customers who value specific features or benefits, enhancing brand loyalty.
- Price Flexibility: Differentiated products can command higher prices because customers may perceive them as offering superior value.
- Market Segmentation: By offering distinct products, businesses can target specific customer segments more effectively.
- Innovation: Encourages continual product development and improvement, keeping the business relevant in changing markets.
The types of product differentiation are:
- Physical Differentiation: Focus on tangible features like design, quality, and performance. For example: Nokia keypad as strongest in quality
- Service Differentiation: Highlight superior customer service or additional services. For example: Butler Service in five-star property
- Price Differentiation: Offer products at different price points (premium or budget). For example Xiaomi phone as budget smartphone
- Image Differentiation: Build a unique brand image or reputation. For example: Iphone as high quality phone
- Location Differentiation: Gain advantage through a convenient or desirable location. For example: Champagne
- Marketing mix is an important aspect of any business. Keeping this in view, explain how many marketing mix are needed for hospitality industry and why they are important. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Marketing mix in hospitality has 8P’s that includes:- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
- People
- Process
- Physical Evidence: Includes tangible aspects (decor, cleanliness, atmosphere). It enhances the service experience and leaves a lasting impression.
- Partnership
The importance of marketing mix are:
- Customer Satisfaction: Optimizes the entire customer experience.
- Competitive Edge: Differentiates from competitors.
- Brand Loyalty: Builds long-term customer relationships.
- Revenue Growth: Attracts and retains customers, boosting sales.
- Adaptability: Allows businesses to adjust to market changes and preferences.
Solved Answers of Year 2019
- What is a relationship between marketing and sales?
→ Marketing generates leads and creates demand, while sales convert those leads into customers, working together to drive business growth.
Hence, the marketing and sales both focus to improve revenue of the organization. - How does service differ from product? (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Services are intangible, inseparable, perishable, and variable, while products are tangible, separable, storable, and consistent. - State the use of secondary data in hospitality marketing? (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ The use of secondary data in hospitality marketing are:- Market Analysis: Understands industry trends and customer demographics.
- Competitor Analysis: Evaluates competitors’ pricing and strategies.
- Customer Behavior: Identifies guest preferences and booking trends.
- Trend Identification: Tracks new travel and tourism trends.
- Benchmarking: Compares performance against industry standards.
- Cost-Effective: Saves time and money by using existing data.
- Forecasting: Predicts future demand and seasonality for better planning.
- What is perceptual mapping? (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2017, Qn no. 9 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - State the consumer problem solving techniques. (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ The consumer problem solving techniques are:- Problem Awareness or Problem Recognition: Customers determines their wants or needs. Identifying a need or problem that requires a solution.
For example: You have exam tomorrow and you don’t have notes also. - Information Search: Gathering information about potential solutions to the problem via online or offline. When consumers finds out their problems and needs, they started looking for information before purchase decision. Several factors must be considered to fully understand this phase:
- Importance of decision
- Amount of prior experience
- Perceived risk: Perceived risk means potential risk that customer has to bear along with purchase decision. It may be financial, social or performance related.
- Sources of information
- Alternative Evaluation: Comparing different options to determine which best meets the needs or solves the problem. Generally alternative has to be evaluated using a single criteria for all alternatives
- Purchase Decision: Making the final decision on which product or service to buy based on the evaluation of alternatives. Various factors may affect like promotions, sales, discounts, salesman approach, etc.
- Post Purchase Decision: Evaluating the satisfaction with the purchase after the product or service has been used. After the usage of product or service, consumers may provide feedbacks, reviews, etc. Positive experience may lead to word-of-mouth marketing also.
- Problem Awareness or Problem Recognition: Customers determines their wants or needs. Identifying a need or problem that requires a solution.
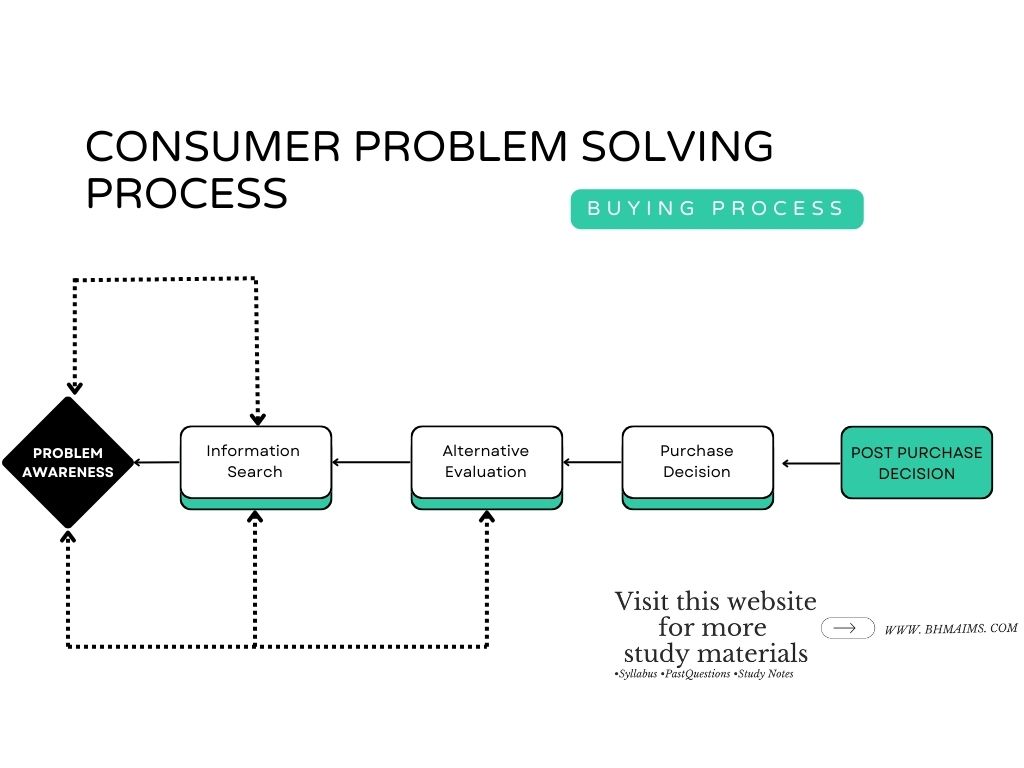
- Define product differentiation. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ → Repeated question from 2018 Question Number 17 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Define a market coverage strategy. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ A market coverage strategy refers to the approach a business takes to reach and serve its target market. It involves deciding how extensively to distribute products or services to maximize market presence and customer reach. This strategy determines the number and type of distribution channels used to deliver products to customers.
Its types includes:- Intensive coverage
- Selective coverage
- Exclusive coverage
- What is tracking studies in marketing? (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Tracking studies in marketing is the strategy in which organization follows consumers to perceive them over a certain period of time rather than in short single point of time. It helps the organization to tracks the changes in consumer behavior and attitudes.
It can be done via:- Maintaining Customer profile : helps to determine heavy (frequent) and light (rare) user of product or services
- Operation Awareness: they are of 3 types – i. top of mind ii. unaided recall iii. aided recall
- Patronage frequency and occasions: determine how often and for what purposes the customers visit to our organization in a certain time period
- Trial purchase
- Advertising awareness and recall
- Customer attitudes and image towards our organization
- Knowledge and usage of key product and services
- Customer preference by occasion
- What is intercept marketing? (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Intercept marketing is a promotional strategy that involves directly engaging consumers at specific locations or events where they are likely to be receptive to marketing messages in real time. - What is the role of intermediaries in distribution of food service? (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Intermediaries in food service distribution facilitate the flow of products from producers to consumers by handling logistics, inventory management, and sales, thereby enhancing efficiency and reach in the supply chain. - What is service marketing and why it is important for the success of a firm in a hospitality industry? (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Service marketing can be defined as the process, practice, act or strategy which promotes the intangible offerings and benefits offered by the business firms to the customers with the aim to build up customer satisfaction, relationship and value.
Service marketing is important for the success of a firm in a hospitality industry because for following reasons:- To build up customer loyalty: Service marketing helps create strong relationships through consistent, high-quality experiences.
- To differentiate from competitors: It highlights unique features and superior service to stand out in a crowded market.
- To enhance brand image: Effective marketing improves the firm’s reputation and attracts more customers.
- To drive word-of-mouth referrals: Positive service experiences lead to customer recommendations and reviews.
- To maximize revenue: Strategic promotions and pricing increase profitability and occupancy rates.
- To meet customer expectations: Ensures services align with and exceed customer needs.
- To improve service quality: Customer feedback is used to continuously enhance the service experience.
- What are the key micro variable in the marketing environment? Explain. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Repeated from 2017, Question number 15 (Please refer back to that year for answer )
The key micro variable in marketing environments are:- Customers
- Employees
- Suppliers
- Intermediaries
- Competitiors
- Public Media
- Technology
- Why is segmentation so significant to effective marketing in hospitality industry? Explain. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Segmentation is so significant to effective marketing in hospitality industry because:- for targeted marketing: like customization of offers and sending the right message to the right group for improved engagement
- to better resource allocation: like focused marketing efforts and reduced wastage
- to offer customized customer experience for improved satisfaction and retention rate
- to enhance customer loyalty: via loyalty programs and building healthy relationships for long-term
- for sake of competitive advantage: encompassing product differentiation and identify niche markets and create unique services or offerings tailored to those segments
- to maximize revenue: via upselling and cross-selling opportunities and dynamic pricing based on demand patterns
- for better adaptation to market changes: quick response to trends and target emerging markets
- for efficient communication via precise message to each market segment and usage of best communication channel
- What is hospitality consumers’ behavior? Explain factors that influence consumer behavior. (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ Hospitality consumers’ behavior refers to the actions and decision-making processes of individuals when seeking, purchasing, and using hospitality services, such as accommodation, dining, and travel experiences. It encompasses their preferences, motivations, attitudes, and experiences, influencing how they choose services, interact with brands, and evaluate their overall satisfaction.
The factors that influence consumer behavior are:- Psychological Factors
- Perception: How consumers interpret and make sense of information about hospitality services. For example, the perception of luxury or value can influence choices.
- Motivation: The underlying needs or desires driving consumer behavior, such as the need for relaxation or adventure.
- Learning: Past experiences and information gained through previous interactions with hospitality services influence future behavior.
- Beliefs and Attitudes: Personal beliefs and attitudes towards travel, service quality, and brand reputation affect consumer preferences.
- Social Factors
- Family: Family needs and preferences play a significant role in decision-making, especially for vacation planning or dining out.
- Friends and Social Networks: Recommendations and reviews from friends, family, or social media influence consumer choices.
- Social Status: The desire to align with a certain social group or status can impact choices, such as opting for high-end hotels or exclusive dining experiences.
- Cultural Factors
- Culture: Shared values, beliefs, and practices that influence consumer behavior. For instance, cultural norms can affect dining preferences or travel habits.
- Subculture: Smaller groups within a culture with distinct preferences or behaviors, such as eco-conscious travelers or luxury seekers.
- Social Class: Economic status and social class influence preferences for luxury versus budget accommodations and services.
- Personal Factors
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level, occupation, and education impact consumer preferences and purchasing decisions.
- Lifestyle: Individual lifestyles and interests, such as health consciousness or adventure seeking, influence choices in hospitality services.
- Economic Situation: Personal financial status affects spending ability and decision-making, including budget constraints and willingness to splurge.
- Situational Factors
- Travel Purpose: The reason for travel, such as business, leisure, or special events, impacts the choice of hospitality services.
- Time: Availability of time and urgency can influence decisions, such as last-minute bookings or long-term planning.
- Occasion: Special occasions or events, like anniversaries or holidays, can affect choices and preferences for services.
- Marketing Factors
- Promotion and Advertising: Marketing messages, promotions, and advertising campaigns can shape consumer perceptions and influence decisions.
- Brand Image: The reputation and image of hospitality brands affect consumer trust and choice.
- Pricing Strategies: Pricing structures, discounts, and value-for-money perceptions play a role in consumer decision-making.
- Technological Factors
- Online Reviews and Ratings: Consumer reviews and ratings on websites and social media platforms significantly impact choices.
- Booking Platforms: Ease of use and functionality of online booking systems and travel apps influence the booking process.
- Social Media: Engagement and influence through social media channels can affect consumer preferences and behaviors.
- Psychological Factors

- Explain the benefits of having a marketing plan for a hospitality industry? (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
→ - Explain management’s role in marketing and sales. (Unit 8: Introduction to Hospitality Marketing and Sales)
→ - What is marketing information system and why it would be useful for a hospitality industry to implement a marketing information system? Explain in detail. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ A Marketing Information System (MIS) is a structured system designed to gather, analyze, store, and distribute information crucial for making informed marketing decisions. It provides a continuous flow of relevant data to marketing managers, enabling them to plan, implement, and control marketing strategies effectively.
The usage of Marketing information System are:- Informed Decision-Making: Provides real-time data for strategic business decisions.
- Understanding Customer Preferences: Analyzes guest behavior and feedback to personalize services.
- Improving Marketing Campaigns: Enables targeted and effective promotional strategies.
- Revenue Management: Supports dynamic pricing and optimizes room rates based on demand.
- Competitive Analysis: Monitors competitors’ activities and market trends for better positioning.
- Enhanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tracks guest loyalty and preferences to improve retention.
- Operational Efficiency: Optimizes inventory, staffing, and resource allocation based on data.
- Market Trend Anticipation: Helps forecast demand and adapt to emerging travel and hospitality trends.
- Cost Control: Identifies inefficiencies, reduces unnecessary expenses, and maximizes profitability.
- Legal and Ethical Compliance: Ensures secure handling of customer data and compliance with regulations (Safety and security)
- “Outgoing calls and incoming calls are the basis for the telephone sales operations” Explain. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Outgoing calls and incoming calls are essential for telephone sales operations:
- Outgoing Calls: Sales representatives initiate these calls to reach out to potential and existing customers or prospect i.e. potential customers, to promote products or services, follow up on leads, which ultimately helps to generate or increase sales. Also, outgoing calls are done to collect feedback and reviews about various products or services.
- Incoming Calls: Customers / clients call in with inquiries, requests, or issues, providing sales representatives with opportunities to address needs, offer solutions, and make sales.
Moreover, each incoming call is an opportunity to engage with a potential customer who is already interested in our product or services, which helps in increasing the chances of converting calls into sales or revenue.
Therefore, sales teams of the company should be well-trained in handling both types of calls (incoming and outgoing), including effective communication techniques. Also, the sales team should have complete information or knowledge regarding product or services offered by the company. Monitoring call activities and outcomes also helps to evaluate the effectiveness of sales strategies and make data-focused improvements.
These call types are crucial for managing customer relationships, generating revenue, and achieving sales targets.
Solved Answers of Year 2021
- Elaborate the meaning of Hospitality service. Explain the major emerging issues and trends of today’s hospitality industries. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Hospitality service refers to the various offerings provided by businesses like hotels, restaurants, resorts, and other service providers to ensure guest satisfaction. For example: Food and beverage service, accommodation service, recreational service, etc.
The major emerging issues are:
a) Environmental impact and sustainability concerns
b) Continued technological changes and keeping up with rapid technological advancements / innovations
c) Balancing personalization with privacy concerns
d) Addressing health and wellness needs of guests
e) Managing the shift towards contactless services
f) Competing with alternative accommodation platforms
g) Ensuring safety and hygiene standards post-pandemic
h) Promoting diversity and inclusion within the workforce
i) Adapting to the rise of remote work and digital nomads
j)Providing authentic local experiences amidst (in the middle of) globalization
k) Constantly changing expectations of customers
l) Political and Security challenges (like terrorism)
The major trends of today’s hospitality industries are:- Sustainability and eco-friendly practices
- Technology integration and advancement
- Personalization and customization
- Health and wellness focus
- Rise of contactless services
- Alternative accommodation options
- Emphasis on safety and hygiene
- Diversity and inclusion
- Digital nomadism and remote work
- Local experience and cultural immersion
- What is consumer behavior? Highlight the nature of hospitality consumer behavior and explain the factors that influence hospitality consumers’ behavior. (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ Factors – Repeated question from 2019 Question Number 14 (Please refer back to that year) - What do you mean by hospitality marketing environment? Highlight its components and define task or semi controllable factors with its nature. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Repeated from 2017, Question number 15 (Please refer back to that year for answer )
Task or semi controllable factors are also called “Micro Environment”. - What do you mean by marketing plan? Highlight its types, also mention the three differences between strategic and tactical plan. (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
→ The types of marketing plan are:
a) Strategic Plan
b) Tactical Plan
The difference between strategic and tactical plan are:
| Basis | Strategic Plan | Tactical Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Long term goals | Short Term Goals |
| Time frame | Typically covers several years (3-5 years) | One year or less |
| Purpose | Establish overall objective or goals for business | Implements strategies to achieve strategic goals |
| Flexibility | More stable; changes infrequently | More adaptable; can change based on immediate needs |
| Decision Making | Involves senior management and long-term stakeholders | Often involves mid-level management and operational teams |
| Risk Evaluation | Considers long-term risks and market changes | Addresses short-term challenges and operational risks |
- What is marketing positioning? Highlight and explain the positioning strategies briefly. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2018, Qn no. 15 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Define hospitality sales distribution and also explain about lodging distribution system. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ - What is COVID 19? How did the pandemic affect the hospitality sectors? Elaborate on the two sector of hospitality industry in Nepal which were largely affected by it. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ COVID-19 is a highly infectious disease caused by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). It was first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, and rapidly spread globally, leading to a pandemic. The virus primarily spreads through respiratory droplets and can cause symptoms ranging from mild (fever, cough, fatigue) to severe (difficulty breathing, organ failure), and in some cases, it can be fatal. Governments around the world imposed lockdowns, travel bans, and strict social distancing measures to control the spread of the virus.
The two largely affected sector of hospitality industry in Nepal were:
a) Hotel industry
b) Travel and Tourism industry
Affects:- Significant decline in tourism
- Heavy revenue loss
- Job losses
- Operational changes: New health and safety protocols, social distancing, and contactless services were introduced to ensure guest safety.
- Business closure: Many smaller business got closed due to prolonged lockdowns and reduced demand.
- High operating costs with little to no revenue.
- Increased hygiene and sanitation requirements post-pandemic leaded increased operational cost
Solved Answers of Year 2022
- Define the term “over-coming the objections” in sales calls. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Overcoming objections in sales calls can be defined as the process of addressing and resolving customer concerns or doubts to persuade or convince them to proceed with the purchase or agreement and have the final sale of product or services. - Define the term out-going calls. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Outgoing calls are those phone calls over telephone which is initiated by a salesperson or representative from a company to reach potential prospect or existing customers with the goal of promoting products or services, following up on leads, or closing sales. - What do you know about “Guest contact areas” of hospitality Industry? (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Guest contact areas in the hospitality industry refer to specific locations or points within a hotel, restaurant, or other hospitality venue where guests interact directly with staff or services. These areas are crucial for shaping the guest experience and influencing satisfaction levels. - What is in house promotion? (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
In-house promotion is the practice of marketing and promoting a company’s products or services internally to employees and existing customers to increase awareness, engagement, and loyalty. - Give the determinant factors of consumer expectation. (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ The determinant factors of consumer expectation are:- Previous Experience
- Word of Mouth
- Marketing Communications
- Service Quality
- Price
- Brand Reputation
- Cultural Influences
- Social Factors
- Situational Factors
- Personal Factors
- What do you mean by limited problem solving process? (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ The limited problem-solving process refers to a decision-making approach consumers use when faced with a purchase that requires more thought than a routine decision but is not as complex or high-stakes as extensive problem-solving. - What is internal merchandising? (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Internal merchandising can be defined as the strategic arrangement and promotion of products within a business environment, including both customer-facing areas and back-of-the-house spaces, to optimize visibility, attract customer interest, and increase sales or revenue by using effective display techniques, signage, and promotional materials. - Point out any two objectives of marketing and sales calls. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Any two objectives of marketing and sales calls are:- to promote new products and services offered
- to collect feedbacks and reviews from the existing product user or service consumer
- Point out the major types of traveler or guests.
→ The major types of traveler or guest are:- Family
- Group
- Leisure
- Business
- Solo
- Luxury
- Budget
- Adventure
- Medical
- What is syndicate research? (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Repeated question from 2017 Question Number 10 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - What do you mean by special service? Explain any three briefly. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Special services are those unique, customized or additional services which are provided by the business which goes beyond standard offerings to meet the specific needs or preferences of the customer.
Explanation of any three are:- Health and Wellness Special Service: It is the special service in which the organization makes a arrangement of various health and wellness related services available to customer as per their needs and preferences.
For example: Hotel BhmAims providing a in-room spa for the VIP guest KP Sharma Oli in his room because of his privacy concern. - Childcare and Family Services: It is the special service in which business organization provides facilities related to child and family. For example: Suppose you visit 5-star hotel BhmAims with you old mother and 5 years old child, if hotel provides you the babysitter and personal caretaker of your mother, then it is supposed to be special services.
- Special Accessibility Services: It is the special service offered to differently abled person. Suppose providing hearing aids or wheelchairs or even a personal caretaker can be supposed as the special service.
- Health and Wellness Special Service: It is the special service in which the organization makes a arrangement of various health and wellness related services available to customer as per their needs and preferences.
- What is market coverage strategy? Explain full coverage market strategy with diagram. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ The full market coveage includes :- Undifferentiated Marketing: One product for entire market
- Differentiated marketing: Different products for different segments
- Concentrated marketing / Niche marketing: Specific products for specific group
- What do you mean by “back of the house”? Explain any four areas, briefly. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ “Back of the house” refers to the operational areas of a business that are not visible to customers but are crucial for managing and supporting daily functions, such as kitchens, storage rooms, laundry facilities, and administrative offices.
Any four back of the house areas are: (Write any 4 of them)- Kitchen: The area where food is prepared, cooked, and plated. Includes cooking stations, storage, and sanitation facilities.
- Laundry: Facilities responsible for cleaning and maintaining linens, uniforms, and other fabrics used in the business.
- Storage: Areas used for storing supplies, ingredients, and equipment. Includes dry storage, refrigeration units, and freezer spaces.
- Administrative Offices: Areas where managerial and administrative tasks are performed, including accounting, human resources, and planning.
- Maintenance Room: Areas where tools, cleaning supplies, and maintenance equipment are stored.
- Dishwashing Area: A dedicated space for cleaning dishes, utensils, and kitchenware.
- Security Office: Central location where security personnel monitor surveillance systems and manage safety protocols.
- Staff Locker Rooms: Facilities where hotel staff can store personal belongings, change into uniforms, and prepare for their shifts.
- Highlight common concern factors of Hospitality research and explain any two. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ The common concern factors of Hospitality Research are:- Customer Satisfaction
- Service Quality
- Market Trends
- Consumer Behavior
- Brand Loyalty
- Operational Efficiency
- Technology Adoption
- Employee Engagement
- Pricing Strategies
- Sustainability Practices
- What are product differences? Highlight and explain any two. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2018, Qn no. 17 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - What is perceptual mapping? Explain it with diagram. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2017, Qn no. 9 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - What is marketing information system? Explain its components and sources. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Definition repeated question
The components of Marketing Information System are:- Internal Records: Information collected from internal company sources such as sales data, inventory levels, customer databases, financial records, and reports from departments like finance and production.
It helps monitor day-to-day operations and understand sales trends, costs, and customer behavior. - Marketing Intelligence: Refers to the collection and analysis of external market data from various sources like competitors, industry trends, and market developments.
It helps businesses stay informed about the market environment and competitor activities, allowing for proactive decision-making. - Marketing Research: Systematic gathering, recording, and analyzing of data related to specific marketing problems or opportunities.
This component uses primary research (surveys, interviews) and secondary research (reports, studies) to understand consumer preferences, market trends, and the effectiveness of marketing strategies. - Marketing Decision Support System (MDSS): A set of tools and software that helps marketing managers analyze data, model different scenarios, and make informed decisions.
It includes statistical tools, predictive models, and data visualization systems that provide insights and assist in forecasting, pricing strategies, and customer segmentation.
- Internal Records: Information collected from internal company sources such as sales data, inventory levels, customer databases, financial records, and reports from departments like finance and production.
The sources of marketing Information System are:
- Internal Data Sources:
- Sales Reports: Sales trends, revenue performance, and customer purchase behavior.
- Customer Feedback: Customer satisfaction surveys, complaints, and product reviews.
- Financial Records: Costs, profits, and financial performance indicators.
- Inventory Management Systems: Stock levels and supply chain efficiency.
- External Data Sources:
- Market Research Firms: Syndicated reports, market analysis, and customer surveys from third-party research firms.
- Public Data: Government reports, industry publications, trade associations, and economic data.
- Competitor Information: Data from competitors’ websites, press releases, annual reports, and industry events.
- Social Media and Digital Analytics: Insights from social media platforms, website analytics, and online customer behavior.
- Primary Data:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Collecting first-hand information directly from customers or target markets.
- Interviews and Focus Groups: In-depth insights from small groups or one-on-one discussions.
- Secondary Data: Like Industry reports and academic journal or publications like research articles
- Marketing research is an important program. It plays an important role in the success of the business. Keeping this in view, describe the process of market research and highlight its importance. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ The importance of market research are:- Informed Decision Making: Provides data-driven insights for strategic decisions. Help the marketing managers, executives, and management make decisions under certainty, uncertainty, and risk. Also, to enhance the tactical and strategic decision-making process.
- Understanding Customer Needs: Helps tailor products and services to customer preferences.
- Identifying Market Opportunities: Uncovers new customer segments or untapped markets.
- Risk Reduction: Minimizes risks by predicting market demand and customer behavior.
- Competitor Analysis: Offers insights into competitors’ strategies and weaknesses. Knowing what the competitors are up to and staying one step ahead of them.
- Effective Marketing Campaigns: Ensures targeted, customer-aligned marketing efforts.
- Product Development: Guides product improvements based on customer feedback.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhances the overall customer experience by addressing pain points.
The research process are listed below:
- Define the Problem or Objective: Clearly state the research goal or issue.
- Develop a Research Plan: Choose research methods, tools, and resources.
- Collect Data: Gather primary (surveys, interviews) and secondary (reports, publications) data.
- Analyze the Data: Identify patterns, trends, and insights from the collected information.
- Interpret and Report Findings: Summarize key insights and offer actionable recommendations.
- Take Action: Implement the strategies informed by the research.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Assess the effectiveness of the decisions and adapt as needed.

Solved Answers of Year 2023
- State the nature of hospitality product and services. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2017, Qn no. 16 (Please refer back to that Year for answer) - Write down the management’s role in marketing and sales. (Unit 8: Introduction to Hospitality Marketing and Sales)
→ The management’s role in marketing and sales are:- Strategic Planning: Develops and implements marketing strategies aligned with business goals.
- Resource Allocation: Allocates budgets and resources for effective marketing and sales execution
- Define the term outgoing cells. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2017, Qn no. 8 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - What is consumer satisfaction? (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2018, Qn no. 8 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Differentiate between primary and secondary research. (Unit 5: Marketing Information and Research)
→ Primary research involves the collection of original data directly from sources through methods like surveys and interviews, while secondary research utilizes existing data that has already been collected and published by others. - Define perceptual mapping. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2017, Qn no. 9 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Highlight the components of 8 Ps. (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
→ The components of 8 Ps are:- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
- People
- Process
- Physical Evidence
- Performance: The measurement of outcomes and effectiveness of marketing strategies and initiatives.
- Define micro environment. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Repeated question - Write about intensive distribution. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Repeated question - Explain the requirements for an effective marketing plan. (Unit 6: Marketing Plan and the 8 Ps)
- Highlight and define the steps of presentation sales call. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ The steps of presentation sales call are listed below:- Preparation: Research the client’s needs and context to tailor the presentation effectively.
- Introduction: Greet the client, introduce yourself and your company, and build rapport.
- Needs Assessment: Ask questions to understand the client’s needs and challenges.
- Presentation: Present the product or service, highlighting how it meets the client’s needs.
- Handling Objections: Address and resolve any concerns or objections the client may have.
- Closing: Request a commitment or decision from the client to finalize the sale.
- Follow-Up: Send a summary, answer any further questions, and maintain engagement.
- Report Making: involves documenting the call’s details, client feedback, and next steps to track progress and plan follow-up actions.
- What is internal marketing? Discuss its benefits. (Unit 9: Hospitality Marketing and Sales Techniques)
→ Repeated Question from Year 2018, Qn no. 13 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Explain the factors that influence hospitality consumer’s behavior. (Unit 2: Understanding the Behavior of Hospitality Consumers)
→ Repeated question from 2019 Question Number 14 (Please refer back to that year) - What are the factors to be considered while selecting a market segment? Discuss. (Unit 4: Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning)
→ - Describe the influence of macro environment on hospitality organization. (Unit 3: Hospitality Marketing Environment)
→ Repeated from 2017, Question number 15 (Please refer back to that year for answer ) - What do you mean by reservation? Highlights its major activities and define the systems in reservation. (Unit 7: Hospitality Sales Distribution System)
→ Reservation refers to the process by which a guest secures a booking for a hotel room, restaurant table, or other hospitality services in advance.
The major activities in reservation are:- Inquiry Handling
- Booking
- Payment Processing
- Confirmation
- Modification
- Cancellation
- Record Management
The systems in reservations are:
- Central Reservation System (CRS)
- Property Management System (PMS)
- Online Booking Engine
- Global Distribution System (GDS)
- Mobile Reservation Systems
- How did COVID-19 affect the hospitality sector? Elaborate on the two sectors of hospitality industry in Nepal, that were badly affected by the pandemic. (Unit 1: Introduction to Hospitality Services Marketing)
→ Repeated question from Year 2021, Question number 7 (Please refer back to that Year for answer)
Practice Questions




