Meaning of Cost Concept and Classification
Cost can be expressed relating with following things:
- It is related with the sacrifice of economic resources.
- It is always expressed in monetary terms.
- It is incurred to achieve specific objectives.
Classification of Cost
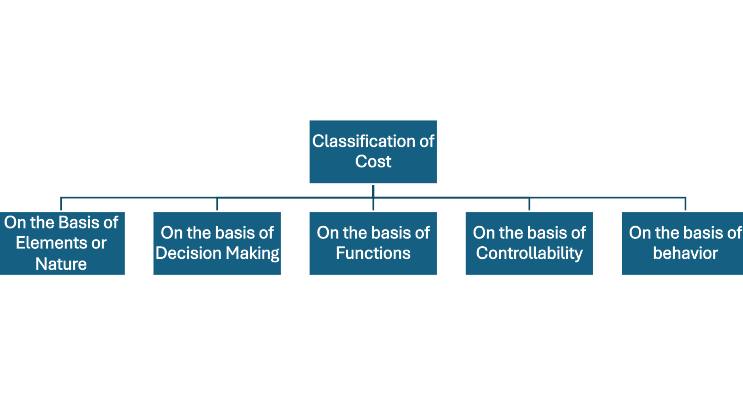
A. On the basis of of Elements / Nature
According to the elements or nature, different cost can be classified into three types:
- Material Cost:
Materials are resources which are needed to produce goods. It is most important part of every production or output. These can be sub-divided as:
a. Direct Materials: These are the main part of finished goods or output. These are easily identifiable to a particular output or product. For example: Wood or steel for furniture, Leather or rubber for shoes, bricks for house construction, etc.
b. Indirect Materials: These are the supportive part of finished goods. These are not easily identifiable to a particular product or output. For example: Glue and thread for making books and copies, button and thread for stitched clothes, etc. - Labour Cost
All the required manpower or human resources which are involved in production and supply of products or goods are known as labour and amount or charges or wages paid to them are known as labour cost. This can also be classified as:
a. Direct labour cost: The cost which are paid for those types of labour who are directly involved in the production process of finished goods. They are easily identified for a particular goods. For example: Wages to tailor for stitching clothes, etc.
b. Indirect labour cost: The costs which are paid to those types of labour who are not directly involved in the production process of finished goods. They are not easily identified for a particular goods. For example: salary to managers, supervisors and auditor, etc - Other Expenses:
All other types of costs other than material and labour are known as other expenses. This can also be subdivided as:
a. Direct Expenses: All the costs which are directly related to production process except direct materials and direct labour are called direct expense or cost. For example: Import duty cost, research and development cost, royalty, etc.
b. Indirect Expenses: All those types of cost which are not directly related to production process except indirect materials and indirect labour are known as indirect expenses or cost. For example: rent, depreciation, insurance, etc.
B. On the basis of of Decision Making
Under this aspect, cost can be classified as:
- Relevant and Irrelevant Cost:
- Opportunity Cost:
- Avoidable and Unavoidable Cost:
- Marginal Cost:
- Differential Cost:
C. On the basis of of Functions
Under this aspect, cost can be classified as:
- Manufacturing or Production Cost:
- Office and Administrative Cost:
- Selling and Distribution Cost:
D. On the basis of of Controllability
Under this aspect, cost can be classified as:
- Controllable Cost:
- Uncontrollable Cost:
E. On the basis of of Behaviors
Under this aspect, cost can be classified as:
- Variable Cost:
- Fixed Cost:
- Semi-Variable Cost:
Segregation of Semi-Variable Cost
Segregation of semi-variable cost can be defined as the act of separating or classifying given semi-variable cost into variable cost per unit (VCPU) and fixed cost.
Methods of Segregation of Semi-Variable Cost
There are 2 methods for segregating semi-variable cost:
- High – Low Methods or Two Point Method
- Least Square Methods
Explanation:
High-Low Method
Step 1: Select the highest and lowest cost (in Rs.) and output / yield / production / level of activity (units, MH, DLH) among the given cost and output units.
Step 2: Calculate Variable Cost Per Unit i.e. VCPU by using below formula:
| VCPU (b) = (High Cost- Low cost) / (High Output – Low Output) |
Step 3: Calculate total fixed cost using below formula:
| Total Fixed Cost (a) = Total cost – VCPU * Output Units or, y = a + b*x |
where,
y = Total Cost
a = Total Fixed Cost
b = Variable Cost Per Unit (VCPU)
x = Units to be produced at the certain desired level of activity
Least Square Method or Statistical Method
According to this method, semi-variable cost is segregated by using the statistical formula. It establishes the mathematical relationship between costs and level of activity.
The following steps are followed in this method:
Step 1: Assume,
X = Output / Production / Level of Activity (Units)
Y = Cost / Semi-variable cost or Mixed Cost (Rs)
Step 2: Prepare Least Square Table
| Observation | Output (x) | Cost (Y) | XY | X2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| xxx xxx xxx xxx | xxx xxx xxx xxx | xxx xxx xxx xxx | xxx xxx xxx xxx | xxx xxx xxx xxx |
| N = xxx | ΣX= xxx | ΣY= xxx | ΣXY = xxx | ΣX2 = xxx |
where,
N = Number of observations or items
X = Output (units)
Y = Cost (Rs)
Σ = Sum of total
Step 3: Find out VCPU by using following formula
| Variable Cost Per Unit (b) = (NΣXY – ΣX * ΣY ) / [NΣX2 – (ΣX)2] |
And also,
| Total Fixed Cost (a) = (ΣY – b* ΣX)/ N |
After calculating VCPU (b) and total fixed cost (a), We can calculate Total cost by using following equation:
| y = a + bx |
where,
y = Total Cost
a = Total Fixed Cost
b = Variable Cost Per Unit (VCPU)
x = Units to be produced at the certain desired level of activity
Introduction to Flexible Budget
A flexible budget is prepared after classifying the costs into fixed, variable and semi-variable as the effectiveness of a flexible budget depends upon the accuracy which the expenses are classified.
Flexible budget is a budget, which is prepared by recognizing the differences between fixed and variable cost, in relation with each level of activities performed.
Features of Flexible Budgeting
- It is related to the ascertainment of total cost and profit at the different level of activities.
- It is future oriented.
- It is more suitable option for the selection of alternative course of actions.
- It is more helpful for the proper utilization of available resources.
Importance of Flexible Budgeting
- It provides different information under different level of activities so that it would be very helpful in preparing a realisitic budget as well.
- It is very helpful in preparing a realistic budget.
- It always provides different suitable basis for the selection of the most suitable alternative out of the available other alternatives.
- It offers various valuable information for effective performance evaluation by management.
Difference between Flexible Budget and Fixed Budget
| Basis | Flexible Budget | Fixed Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | It is flexible and can be changed or updated quickly according to level of activity done. | It is rigid i.e. not flexible and doesn’t change. |
| Condition | It is made to change according to conditions or situations. | It is made assuming that condition would remain static. |
| Classification of Cost | Cost are classified according to the nature or their variability. | Cost are not classified according to their variability i.e. fixed, variable and semi-variable. |
| Forecasting | It clearly shows the impact of various expenses on the operational aspect of the business. | It is difficult to forecast accurately the results in it. |
| Budget | Series of budgets are prepared at different levels of activity, under it. | Only 1 budget at a fixed level of activity is prepared. |
| Ascertainment of cost | Costs can be easily ascertained at different levels of activity under this type of budget. | It is not possible to ascertain costs correctly if there is a change in circumstance. |
Methods for Preparing Flexible Budget
There are following methods of preparing flexible budget which are as follows:
Formula Method
To determine the total cost of a given level of activity, the following flexible budget formula can be used:
| BA = FC + UVC * LA |
Where,
BA = Budget Allowance i.e. Total Cost at the given level of activity
FC = Fixed Cost
UVC = Unit Variable Cost
LA = Units to be produced or required at the given Level of Activity
Alternatively,
The following regression equation can also be used for this purpose:
| Y = a + bx |
Where,
Y = Total estimated cost
a = Fixed cost
b = Variable Cost per unit (V.C.P.U)
x = Units to be produced or required at the given Level of Activity
Tabulation Method
We can prepare flexible budget by using tabulation method also. This can be done in two ways as shown below:
- Without showing the semi-variable cost separately. Under this, the semi variable costs are segregated into variable cost and fixed cost and shown them in their respective heading i.e. fixed and variable.
……. Company
Flexible Budget


- Showing the semi variable cost separately. Under this, the semi variable cost are segregated into variable cost and fixed cost and the semi variable cost for different levels are calculated shown under its headings as shown below:
……. Company
Flexible Budget