









Introduction to Fire
Fire can be defined as the rapid oxidation-reduction reaction resulting in the production of heat and, generally, of visible light in the form of luminous flame.
(Or)
Fire is a rapid chemical reaction called combustion, where a material (fuel) reacts with oxygen, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products such as gases and smoke.
Elements of Fire
The elements of fire are:
- Fuel
- Heat
- Oxygen
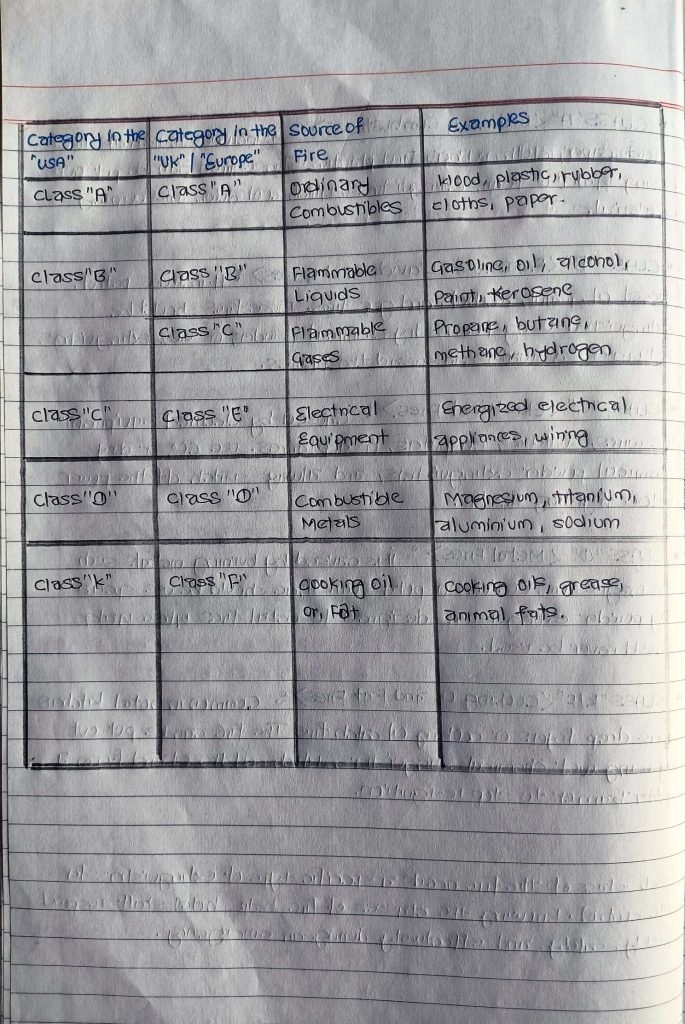
The fire triangle is a simple model used to explain the three essential elements required for a fire to ignite and sustain itself:
All three elements must be present for a fire to occur. If any one is removed—by cooling (removing heat), smothering (removing oxygen), or starving (removing fuel)—the fire will extinguish. This is why the fire triangle is used to understand how to prevent or control fires.
Explanation:
- Fuel: Any material that can burn, such as wood, paper, or gas. Fuel provides the substance that is combusted in the fire. Fuel can also be defined as a substance that acts a reducing agent.
A reducing agent gives up electrons to an oxidizer, which is capable of accepting electrons, resulting in a compound consisting of the fuel and the oxidizer. When a fuel reacts with an oxidizer, we say fuel is burning. This reaction releases heat and visible light. When this happens very fast with rapid and large amount of heat and visible light, we say that fire has occurred.
| Simply, fuel can be defined as a substance which gives off heat and/or light for useful purposes when it is burnt. |
A fuel may be an element such as oxygen, hydrogen, magnesium or compound such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons such as methane, propane, butane, etc. It may also be a complex organic compound such as firewood, coal, jute, cotton, rubber, natural gas, petroleum, etc. Methane, propane, and butane are used as cooking gases. Commercial liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a mixture of propane and butane.
- Oxygen: It can also be referred as “oxidizer”. The fire requires an oxidizing agent, typically oxygen from the air, to sustain the combustion process.
Oxidizer is one of the most important component for burning fire. Besides oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc., are also strong oxidizers. - Heat: Heat is necessary to raise the fuel to its ignition temperature, the point at which it starts burning. Once a fire starts, heat continues to sustain the combustion process.
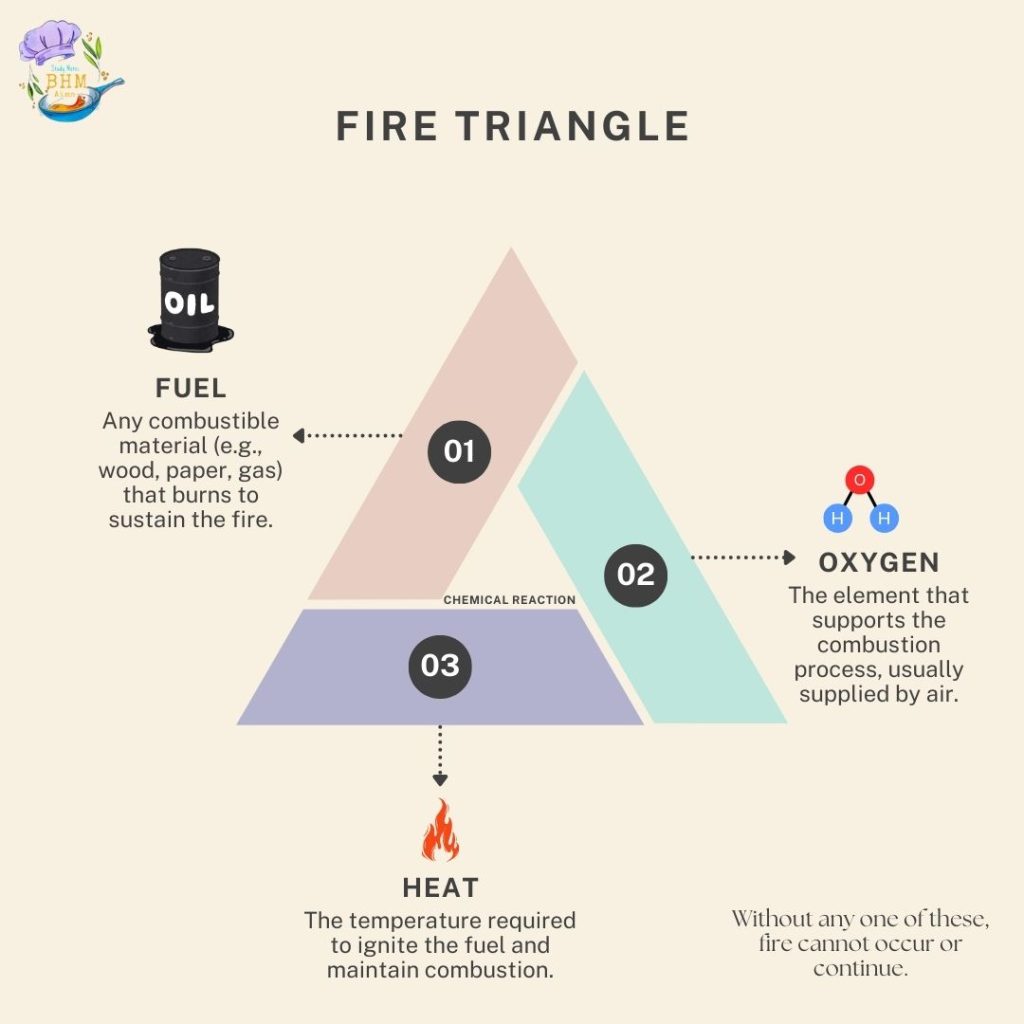
The Fire Pyramid (or fire tetrahedron) expands on the traditional fire triangle by adding a fourth element: a chemical chain reaction. The four components of the fire pyramid are:
- Heat
- Fuel
- Oxygen
- Chemical Chain Reactions: The chemical chain reaction in the fire pyramid refers to the self-sustaining process that occurs during combustion, where heat, fuel, and oxygen continuously interact to produce more heat and sustain the fire.
During combustion, the fuel breaks down into smaller molecules, releasing free radicals—highly reactive particles. These free radicals interact with oxygen in a series of reactions that produce more heat and more free radicals, keeping the fire going. This chain reaction ensures that the fire can propagate, as the heat generated keeps providing the energy necessary to sustain the burning process.
Ways of extinguishing burning fire
To extinguish fire, one or more of the more of the following steps should be taken:
- Removing / limiting the supply of oxygen by
- Preventing air from entering the fire-zone air, e.g. blanketing by water mist, non-flammable gases, etc.
- Shutting the lid over a burning fuel tank or putting foam to prevent entry of fresh air
- Diluting air with a non-oxidizing gas such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen, etc.
- Stopping supply of fuel: By mechanical means e.g. diverting the fuel or closing the supply line valve
- Removing heat: By way of cooling the burning materials below the ignition point with a suitable cooling agent
- Interrupting the chemical chain reaction of fire
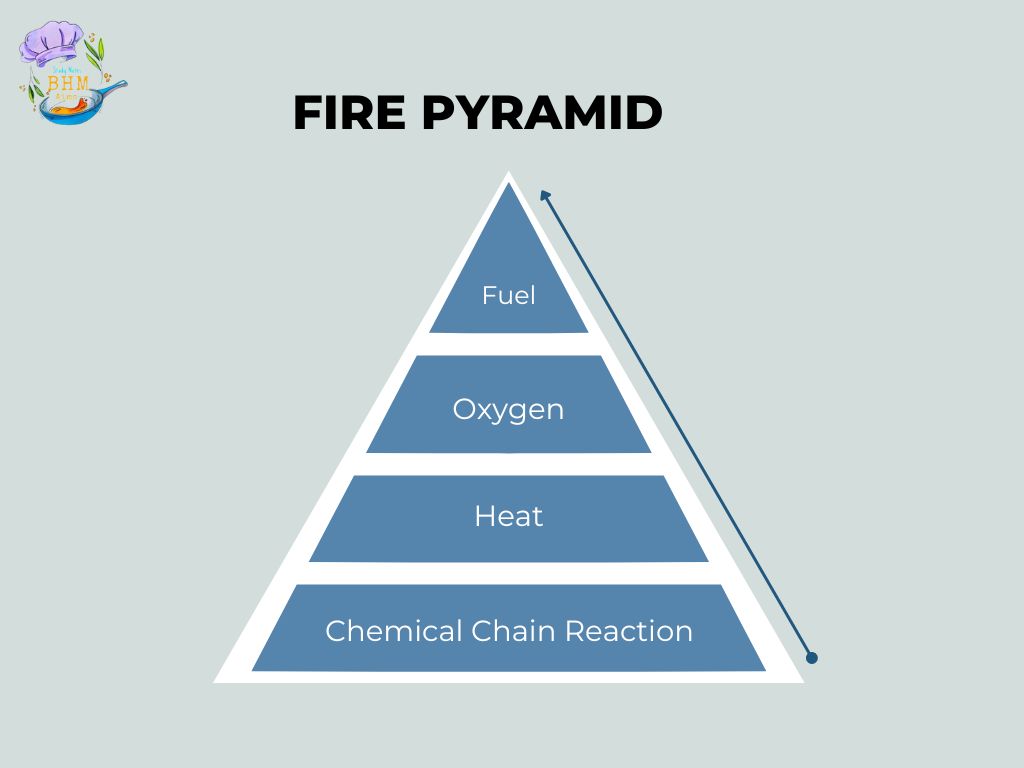
Classes of Fire
Fire is classified depending upon the type of fuel / combustibles involved and the source of heat.
| Category in the USA | Category in the UK / Europe | Fuel / Source of Fire | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Class A | Ordinary Combustibles | Wood, paper, cloth, plastics, rubber |
| Class B | Class B | Flammable liquids | Gasoline, oil, alcohol, paint thinner, kerosene |
| Class C | Flammable gases | Propane, butane, methane, hydrogen. | |
| Class C | Class E | Electrical equipment | Energized electrical appliances, wiring |
| Class D | Class D | Combustible metals | Magnesium, titanium, aluminum, sodium |
| Class K | Class F | Cooking oil or Fat | Cooking oils, grease, animal fats |
Fire Protection Device
A fire protection device is equipment, tool or system designed to detect, suppress, or control fires, providing safety for both people and property. Here are key types of fire protection devices:
- Detector Systems
- Heat Detectors
- Smoke Detectors
- Fire Sprinkler System
- Fire Alarm System
- Fire Extinguisher
- Fire Blanket
- Fire Doors
- Emergency Exit Signs and Lightning
Explanations:
- Detector Systems: Fire are often first detected by human observation. But methods of detection that operate independently of human presence are also very much essential. Fire detectors may respond to any one or other of the manifestations of combustion, such as the generation of heat, smoke, and flames.
There are various types of detector systems used for safety and security because no single detector is suitable for all types of conditions.- Heat Detectors:
Heat detectors are fire alarm system that work on the principle of sensing heat source by way of measuring temperature and/or rate of rise of temperature.
If the rate of
- Heat Detectors:
Fire Extinguishers and its Types
A fire extinguisher is an active fire-protection device. It is normally a manually operated and typically a hand-held device (a cylindrical or conical pressure vessel), which produces fire-resistant agents and can be discharged to extinguish a fire.
These are to be used to extinguish or control small fires only, often in emergency situations. It is not much useful when the fire is out of control.
The types of fire extinguisher are:
- Water type
- Foam type
- CO2 type
- Dry chemical powder (DCP) type
- Halogenated hydrocarbon (HALON) system
- Wet chemical type
Sources of ignition and prevention (Causes and Prevention of Fire)
There is a saying “Prevention is better than cure” which is very useful in case of fire also. A few common sources of fire and their possible methods of prevntion are listed below:
- Electrical equipment: Electrical defects are generally due to poor maintenance, e.g. short circuits, etc. Preventive maintenance of equipment and regular checking method
Example of causes: Faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, and malfunctioning appliances. - Friction: Defects occur due to hot bearings, misaligned or broken parts, jamming of materials, etc. Following a regular schedule of inspection, maintenance and lubrication is needed.
- Open flames: Gas cutting and welding of material may result in fire in an inflammable environment. Follow the rules of welding and gas cutting. Use of open flames near combustibles, such as cotton waste, paper, grease, etc., should be strictly avoided.
Example of causes: Unattended candles, stoves, or matches. - Smoking: Smoking is dangerous near flammable material. Smoke only in permitted areas.
- Hot surfaces: Exposure of combustibles to furnaces, hot ductsm or glowing elective lamps or irons, etc is dangerous.
- Chemical Reactions: Improper handling or mixing of chemicals can lead to fire. Follow safety guidelines for storing and using chemicals to prevent dangerous reactions.
