POULTRY
INTRODUCTION
Poultry word comes from the Latin word ‘Poule’ which basically means to hang. This term also refers to the flesh of such birds.
Poultry refers to any domesticated avian species such as chicken, turkey, goose, etc. which are generally raised for eggs, meat, and/or feathers. Especially, they are domesticated / raised in farms by confining them in limited areas and restricting their movement so that they can grow faster for the production of eggs or meat.
Poultry is highly nutritious meat as it is classified as a complete protein and also it falls into the category of white meat and after fish, it is one of the leanest meat available. It is recommended that fresh poultry should not be used directly. After being slaughtered, it must be hung by the legs in refrigerator or any cold temperature rooms for at least 24 hours so to make it tender. If the poultry is frozen, it should be thawed to avoid any possible food poisonings.
NOTE: Thawing is a specific term which is used to describe the process of taking a frozen product from frozen to a temperature (usually above 0 Celsius) where no residual ice is left, i.e. defrosting. Simply, it is just opposite process or reversal of the freezing product.
TYPES OF POULTRY
1. Chicken (Poulet)
For various purposes, including laying, meat, and/or dual-purpose production, numerous different breeds of chickens have been developed. For instance, including many other breeds, broilers which are raised for meat, and layers breed are raised for eggs. White and dark flesh are both present in chicken, which contains less fat when cooked skinless. It is versatile, affordable, easily accessible fresh or frozen, and may be prepared in a variety of ways.
Classification of chicken
| Poussin | Spring Chicken | Broiler / Roaster | Boiling Fowl | Capon |
| Chicken weighing 300-400 gram of 3-4 weeks | Chicken weighing 400-500 gram of 6-8 weeks old | Between 1-1.5 kg and even to 9 week old | A mature hen of 1 year of age and weighing between 1.5-2 kg | Castrated male roosters, that are 4-5 months old an weighing between 3-4 kg |
Q.N. Define Capon.
ANSWER:
A capon is a male chicken that has been neutered or castrated, removing its genital organs to enhance the flavor of its flesh. It is castrated, either physically or chemically, to make the meat more tender and less gamy (that is, with a strong flavor or odor).
It’s age is over 10 months (to be consumed) and has 4-6 lb (i.e. 1.8-2.7 kg). Also, it has coarse skin, tough and dark meat.
2. Turkey (Dinde)
Turkey( Dinde: In French ) is typically a popular domesticated bird which are primarily raised for their meat, and is highly popular dish of poultry, especially in North America, where it is consumed traditionally as cultutrally important occasions portion such as christmas and Thanks-giving meal feast. They often weigh more than chickens and make an audible “quack.”
It is sold sliced and grounds as well as ” whole” in a manner similar to the chicken with head and feets removed. The average weight of bird may range between 3-11 kg and when prepared without the skin, it has white, dark, meat and also contains little fat.
3. Ducks ( Le Canard)
Ducks are also commolnly known as waterfowl as they spend so much of their time around places with water. Hence, duck (canard: in French) is a medium sized domesticated aquatic birds in the family Anatidae which is generally with smaller and shorter neck than swans and geese, short legs set far back on the body, webbed feets and eyes on the side of the head.
Ducks come in a variety of breeds, including Barbary, Peking, Nantes, and Rouen. The duck which is three months old is known as a Carad. The skin and fat are typically left on when grilling a deboned duck breast, just like you would a steak. Internal organ such as heart and kidneys are also eaten and the liver in particular is often to prepare Foie gras. It has dark meat and have a distinctive “gobble” sound.
4. Squab ( Pigeonneau)
The term “squab” refers to an immature domestic pigeon, or nestling pigeon, which is typically under 4 weeks old and weighs 500–600 grams.
Before being butchered, squab are raised for about three to four months, until they reach adult size but have not yet flown. Squab is much darker, very tender, moist, and delicious than many regularly eaten poultry meats in cuisine; its meat is typically regarded as a very flavorful, delicacy.
Squab is a common ingredient in North Eastern Indian cuisine, including Assamese curry. As a result, it is utilized in many nations’ cuisines, including those of France, Italy, Egypt, the United Kingdom, Northern Africa, and various Asian nations. It can be prepared in a variety of culinary styles, including pan-frying, roasting, grilling, and braising. It is also often served with a variety of side dishes, such as grains, root vegetables, or fresh salads.
It constitues a high protein and nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin B12. Also, it has relatively high fat and calories compared to other types of poultry.
5. Goose (Oie)
A goose is larger than a duck, has webbed feet, a longer neck, and makes a distinctive “honking” sound.
In order to make the flattened liver known as foie gras, it is primarily cord-fed and forced-fed. Both domesticated and wild varieties can be found. The meat, eggs, and feathers of the birds are bred as food. Although not as fatty as duck, goose flesh is dark and fatty. Up to 8 kilograms can make up a goose. It is typically roasted and has very fatty dark meat.
| ENGLISH WORD | FRENCH WORD | |
| 1. | Chicken | Poulet |
| 2. | Duck | Canard |
| 3. | Turkey | Dinde |
| 4. | Goose | Oie |
| 5. | Guinea Fowl | Pintade |
| 6. | Squab | Pigeonneau |
CUTS OF POULTRY AND USES
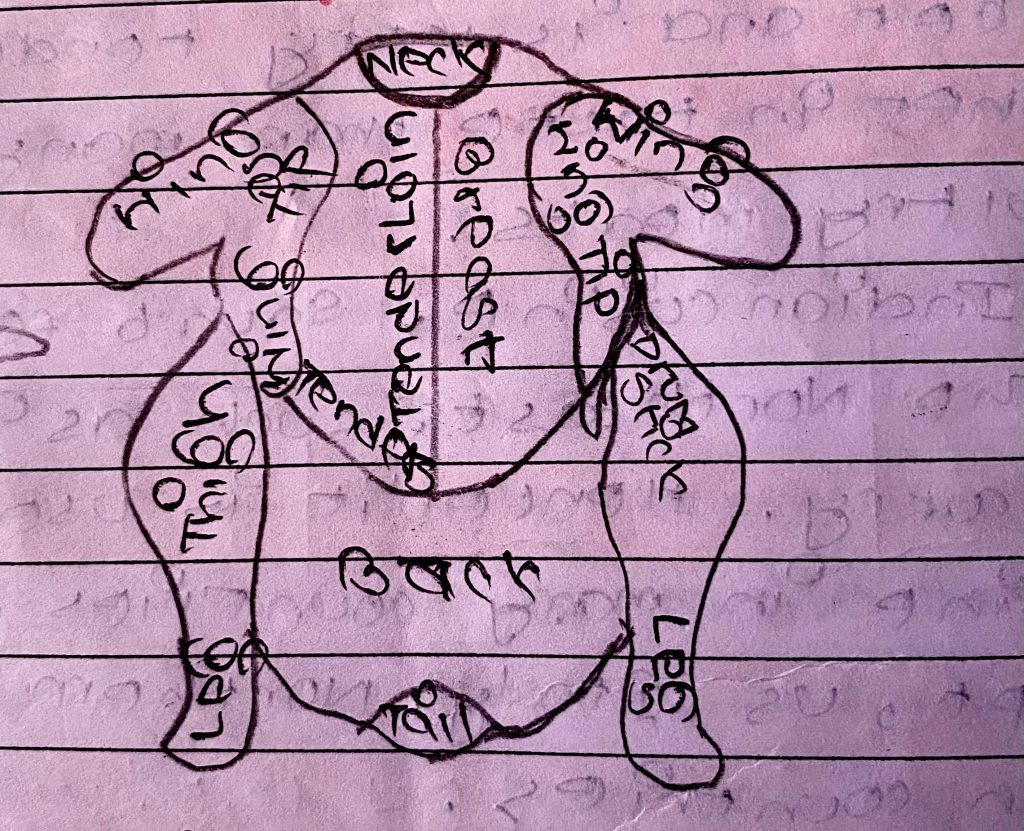
1. Wings (French: Aile)
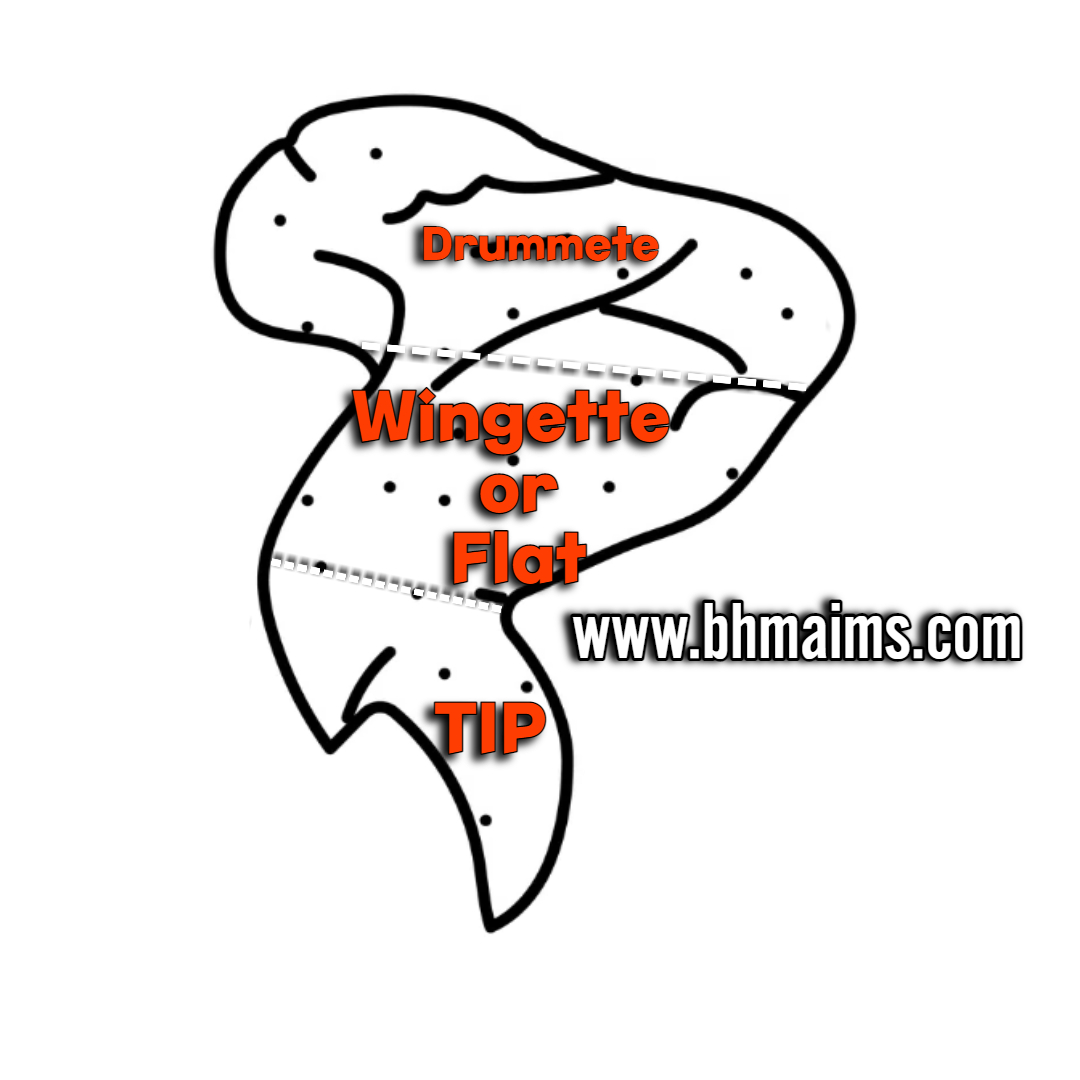
Description: The whole chicken wings is produced by cutting the wing from a whole bird without giblets at the joint between the humeurs and the backbone. And the whole chicken wing is an all-white meat portion composed of thhree sections; drumette, mid-section, and tip.
This is the cut having wings bone and flesh attached to it. FLesh is delicate and juicy, ideal for most types of cooking methods.
Usage: It is generally used in preparatrion of lollipop, brarbecuing with bone.
2. Thigh (French: La cuisse)
Description: The area of the leg that connects the hip and knee is known as the thigh. Similar to the drumstick, the thigh flesh is black and flavorful. It has a nice firm and juicy texture and is just as versatile as its leg counterpart. It can be prepared as thigh cutlets with bone and skin still attached, or as a thigh fillet with skin and bone removed. It is a light brown color and contains more fat than breast.
Usage: It can be roasted, grilled or fried and is often used as stew, curry and for deep frying.
3. Breast (French: Sein / Poitrine)
Description: The breast is the large, meaty part of the chicken that sits on the top of the ribcage. It can be obtained wither boneless or with rib cage bone attached to them. It is a white meat with a very little fat.
Usage: Chicken breast must be most versatile meat. Firstly, it can be cooked whole, sliced into cutlets, or diced into smaller pieces. Also, it is perfect for grilling, pan frying, sauteing or deep fried. It can also be baked or poached and used in salad, sandwiches or shredded and put in soups.
4. Drumsticks (French: Pilon)
Description: Drumstick inclueds the lower portion of the leg quarter (the portion between the knee joint and the hock). This portion of meat is dark in color and it is also regared as one of the fattiest parts of the chicken.
Usage: It is juicy and mostly used in deep frying and barbecuing.
5. Fillet (French: Filet / Filet de)
`Description: The supreme component of chicken, or the filet, is joined to the bird’s breast. The chicken’s tenderloin, or “supreme,” is incredibly soft and lean. A boneless, skinless portion of the breast is called a filet.
Usage: Chicken fillets are a common ingredient in many chicken-based recipes and are frequently used in sandwiches, salads, and stir-fries. Grilling, mincing, sautéing, and barbecuing are all done with it.
6. Carcass (French: Carcasse)
Description: Carcass of a chicken is the leftover body after most of the meat has been removed. It consists of the skin, bone, cartilage and some meat (i.e. residual meat) that may be left on the bones.
Usage: It is mostly used in stock preparatrion, i.e. chicken stock, which is highly flavorful liquid used as a base for various dishes, soups, stews, and sauces.
(Point 7 and 8 can be commonly called as Giblets. Giblets are the edible organs of differents poultry, such as the liver, heart, gizzard annd neck. Giblets are mostlyused to add flavor in stocks, soups and gravies.)
7. Liver (French: Foie)
Description: Liver is a reddish-brown organ that has distinctive flavor and teture, and is high in protein, iron, and other nutrients. Liver of a goose is used in preparation of foie gras, often in some country like China, liver, heart, gizzard and feet of the poultry are commonly eaten.
Usage: It can be cooken in various ways, such as sauteing, frying or also often used to make pates or added to the dishes like stir-fries, soups, or stews for extra flavor and nutrition to the dish.
8. Neck (French: Cou)
Neck is a bony part of the chicken that connects the head to the body.
Usage: The neck part is often used for stock preparation as fat content is very low. It is oftem used to add flavors to stocks, soups and gravies, as it contains a lot of collagen, which adds aroma and create a rich and flavorful broth.
QUALITY SIGNS OF POULTRY
There are few points to be considered to ensure the poultry is healthy and safe enough for human consumption. Here are some of the key quality signs to look for when purchasing or consuming poultry:
a. Eyes
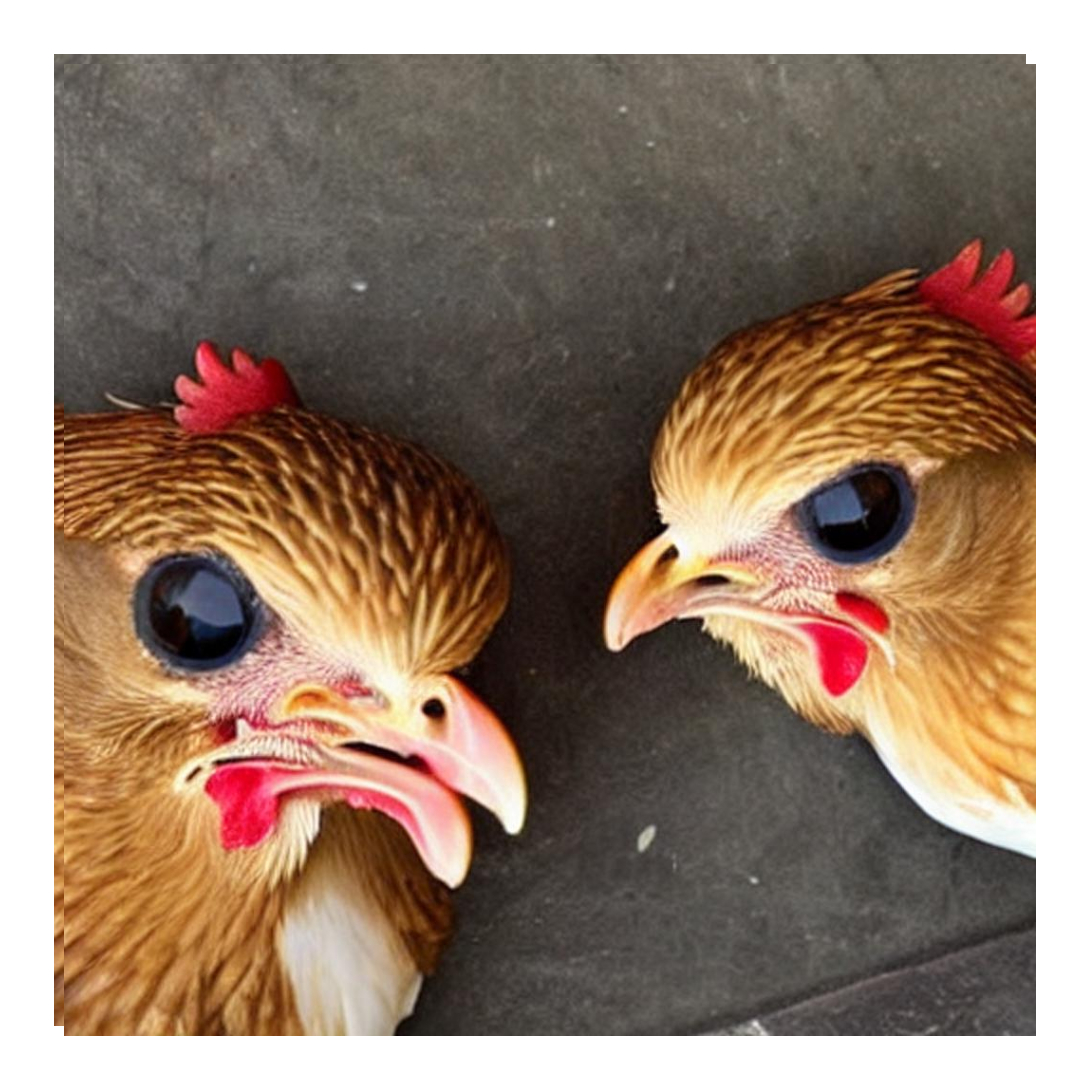

The eyes appearance canalso be a quality sign of poultry. When inspecting poultry, eyes should be clear and shiny and should not be cloudy or sunken, which can indicate the unhealthy and unsafe bird sign for human consumtion. When a chicken is alert and active, it’s eyelids should not be showin. Additionally, there should not be any discharge or crust, as this can be a sign of various infection to the bird.
b. Nose
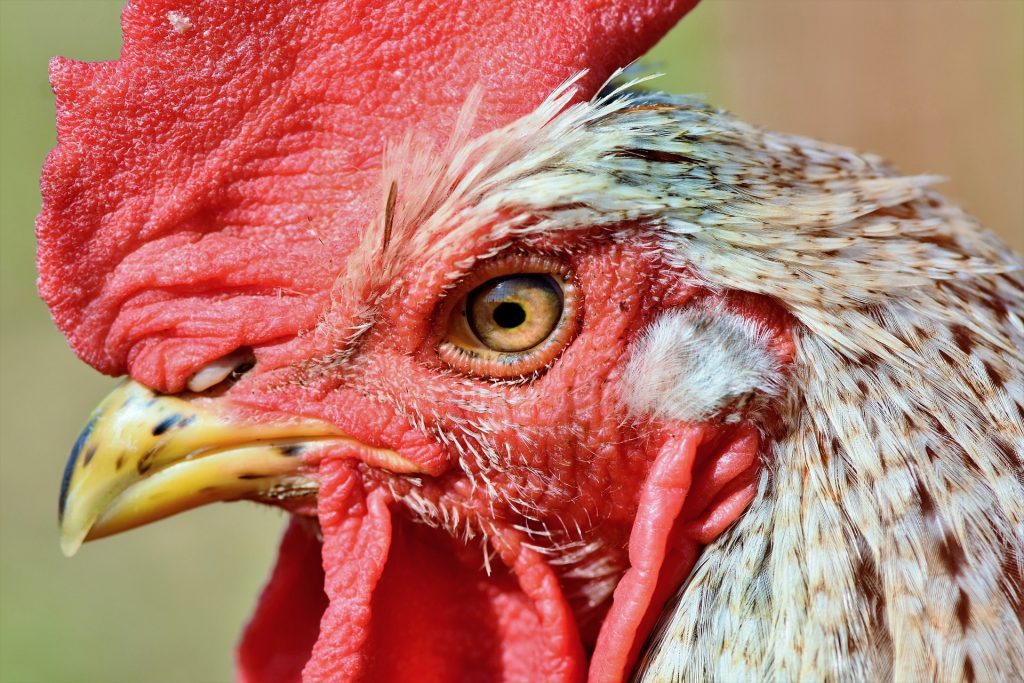

Though, poultry don’t have a typical nose like humans do, they do have a nasal opening on their peak.
Unless in extremely heated situations, breathing via both nostrils should be done with the mouth shut. If cooling the bird does not force it to breathe via its mouth, it may be an indication of sick or contagious poultry.
c. Wings

In most breeds, chickens should be carried with their wings close to their bodies. Several breeds have downward-pointing wings.
In addition, the wings should be adequately formed, properly proportional to the rest of the bird, and injury- and deformity-free. The wings’ feathers should be free of any indications of injury or loss, and they should be clean and bright.
The age of the bird can also be ascertained from the wings when assessing the quality of poultry. Juvenile birds have wings that are softer and more flexible, but adult birds have wings that are more rigid and less flexible.
d. Feathers
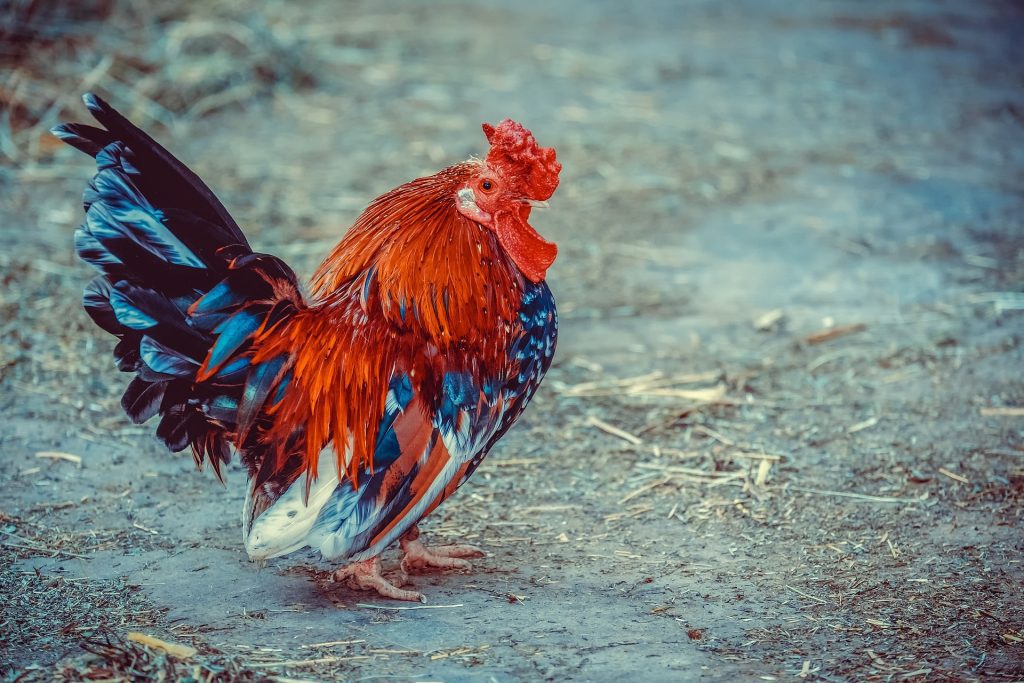

A healhty bird has its feathers smoothed down when it is active. As wings, the age of the bird can also be ascertained from the feathers when assessing the quality of poultry. Juvenile birds have feathers that are softer and more flexible, but adult birds have feathers that are more rigid and less flexible.
e. Vent
The vent, which is a bird’s external opening to its digestive and reproductive systems, can also be an indicator of good poultry. The vent should be clear, dry, and devoid of any discharge or inflammation in healthy birds. A filthy or enlarged vent may indicate a bacterial infection or other health issues.
f. Mental state

Mental state refers to the overall well-being and psychological state of an animal including its behavior, mood and mental health.
A healthy bird will display typical actions including feeding, drinking, and exploring its immediate surroundings in addition to preening (straightening and cleaning its feathers with its beak). Also, it exhibits typical social activities with other birds, such as interacting with them and displaying signs of contentment. Also, the poultry should appear alert and active trying to avoid strangers.
When we try to catch the bird, it will be easy to handle if it is sick. Moreover, birds with poor mental health may display odd behaviors including aggression, fear, or lethargy, as well as feather pecking, which is the act of biting or striking one’s own feathers with the beak.
POINT-WISE:
- The flesh and skin should be white with fine texture.
- Breast bone should be fine and flexible at the vent end.
- The meat of the poultry shouldn’t smell unpleasant. It should be fresh.
- The skin of the poultry should be unbroken with no bruising or discolouration. The colour of the skin should be white for chicken an creamy white for duck, turkey and goose.
- Breast should be plump, not bruised or discoloured.
- Spurs showing no sign of development.
- Poultry should have scales on leg tight, fine and even.
- It is advised that poultry should be bought frozen.
STORAGE OF POULTRY
The storage of poultry involves proper handling and storage of raw or cooked poultry to ensure its ensure itd safety and freshness. Here are some guidelines for storing poultry:
Fresh poultry must hang on drawn for 24 hours in a cool room.
- Fresh poultry can be stored for 3 or 4 days at atemperature below 3 degree celsius.
- For the longer storage, birds must be in frozen stage. Frozen poultry are best for used upto 6 month if it kept in temperature between -18 degree to -22 degree celsius.
- Poultry is best kept on the bottom shelf of the cool room, which is the coldest area, and arranged on drip trays to catch any juices that seep out during storage. These trays should be cleaned regularly as part of your ongoing chicken kitchen hygiene.
- To prevent contamination and food cross-contamination, raw poultry should be stored in leak-proof containers or wrapped in plastic wrap or aluminum foil. Moreover, cooked poultry needs to be tightly wrapped in foil or kept in airtight containers.
- Frozen poultry should be thawed in the refrigerator, in cold water or in the microwave. Prior to cooking, it is crucial to make sure the poultry is fully thawed.
By following these guidelines, the storage of poultry can be done safely and effectively, ensuring that it remains fresh and safe for long time.
