Past Year Question Paper


Previously, the same syllabus was included in the 5th semester under the title “Facility Planning and Management.” However, after the Tribhuvan University syllabus update, it has now been revised and included in the 4th semester as “Hotel Engineering.”
The following are the past-year board questions that were asked when this subject was offered in the 5th semester.
Facility Planning and Management Year 2018 Question Paper
Facility Planning and Management Year 2019 Question Paper

Facility Planning and Management Year 2021 Question Paper

Facility Planning and Management Year 2022 Question Paper

Facility Planning and Management Year 2023 Question Paper


| Dear Students, If you find any question paper missing from any year, please contact us through our email address “bhmaims@gmail.com“ Also, if you have any missing past-year board question papers, kindly forward them to us so that we can update in our website. |
Solved Answer
Solved Answer of Year 2018
- What is live load in a building? (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ A live load in a building can be defined as the non-permanent, movable weight that a structure must support during its everyday use.
For example: people, furniture, and equipment, which can vary in position and amount over time.
नेपालीमा भन्दा, Live load भनेको मानिसहरू, furniture, र equipmentजस्ता temporary वा चलायमान weight हो, जुन buildingले यसको प्रयोगको क्रममा weight bear गर्नुपर्ने हुन्छ। यो load permanent हुँदैन र समयसँगै बदलिन सक्छ। - Briefly write on rainwater harvesting. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use, typically for irrigation, household use, or groundwater replenishment.
नेपालीमा भन्दा, आकाश बाट परेको पानीलाई पछि कुनै कामको लागि जम्मा गर्ने तरिका is called rainwater harvesting- खेतमा बिरुवाहरुलाई हाल्न सकियो, भाडा धुन सकियो, - Define capital project cost. (Unit 3: Hotel Building Economic)
→ Capital project cost refers to the total expenses incurred in the development or renovation of a hotel building, including costs for land acquisition, construction, architectural and engineering fees, equipment, and other expenditures necessary to complete the project and bring it into operation. - What is grey water? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ Grey water is the relatively clean wastewater generated from sinks, showers, and washing machines, excluding water from toilets. It can be recycled for uses such as irrigation and flushing toilets, reducing the demand on fresh water supplies. - List out the different type of protective device. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The most common protective devices include:- Fuse – Breaks the circuit when there’s excessive current.
- Circuit Breaker – Automatically cuts off power during overloads or short circuits.
- Surge Protector – Shields devices from voltage spikes.
- Residual Current Device (RCD) or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) – Protects against electric shocks by detecting current leakage.
- Lightning Arrester – Diverts lightning strikes away from buildings to prevent damage.
- What is HVAC system? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heating, ventilation and Air conditioning)
→ An HVAC system (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) is a technology used to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality within buildings. It ensures indoor comfort by providing heating during cold conditions, cooling during hot weather, and proper ventilation to circulate fresh air and remove contaminants. - What are different components of refrigeration cycle? (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ The refrigeration cycle consists of several key components that work together to transfer heat and provide cooling. The main components are:- Evaporator – Absorbs heat from the surroundings and cools the refrigerant, causing it to evaporate into a gas.
- Compressor – Compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser – Releases the absorbed heat to the outside environment, causing the refrigerant gas to condense into a liquid.
- Expansion Valve – Reduces the pressure of the refrigerant liquid, allowing it to expand and cool before entering the evaporator again.
These components work in a continuous loop to remove heat from the desired area and maintain a cool temperature.
- Write the full form of LED. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heat & Light)
→ The full form of LED is ‘Light Emitting Diode’. - What is clean energy? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Fuel)
→ Clean energy refers to energy sources that produce little to no pollution or greenhouse gas emissions during their generation and use. Examples include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy, which contribute to reducing environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels. - Define Fire drill. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ A fire drill is a practice exercise conducted to prepare building occupants for an emergency evacuation in case of a fire. It involves simulating a fire situation to ensure that everyone knows their escape routes and procedures, and to test the effectiveness of the building’s fire safety systems. - What is maintenance of a hotel and how is it important? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Maintenance)
→ Maintenance is the systematic process of ensuring that equipment, systems, buildings, and other assets are kept in optimal working condition through regular inspections, repairs, adjustments, and preventive measures. It involves a series of activities aimed at preserving the functionality, safety, and efficiency of the assets over their lifespan.
Maintenance is importance because for following points:- It ensures guest satisfaction and comfort.
- It maintains safety and regulatory compliance.
- It enhances operational efficiency.
- It prevents costly repairs and reduces downtime.
- It extends the lifespan of assets.
- It upholds a positive brand image.
- Explain the important consideration while designing a lobby in a hotel. (Unit 2: Design & Planning)
→ The important consideration while designing a lobby in a hotel are: (write any 5 points)- Warm First Impression: The lobby is the first area guests gets entrance, so its design should be welcoming, stylish, and reflective of the hotel’s brand identity so it sets the tone for the entire guest experience.
- Proper Utilization of Space: The layout should efficiently accommodate check-in/check-out areas, seating, and traffic flow, making sure of comfort and convenience. It should also provide sufficient space for guests to move freely without congestion.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The lobby design should have an inviting atmosphere with aesthetically pleasing elements such as modern furniture, art pieces, lighting, and color schemes that matches with the hotel’s theme and target clientele.
- Functionality: The lobby should have practical amenities such as comfortable seating, reception counters, luggage storage, and clear signage. It should also accommodate services like concierge desks, business centers, and café or bar areas if applicable.
- Lighting and Ambiance: Proper lighting, both natural and artificial, enhances the ambiance. Bright, well-lit spaces make the area feel welcoming, while mood lighting can create a cozy and luxurious atmosphere in the evening.
- Acoustics and Noise Control: The design should account for noise reduction through sound-absorbing materials in ceilings, floors, and walls, ensuring the lobby remains peaceful despite high traffic.
- Comfort and Accessibility: The lobby should be designed to be easily accessible for all guests, including those with specially-abled people. Features like ramps, elevators, and wide entryways ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
- Safety and Security: The lobby should be designed with security in mind, including surveillance systems, emergency exits, fire safety equipment, and a clear line of sight for staff to monitor the area.
- How does HVAC system work and why is it so important in the operation of a hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heating, ventilation and Air conditioning)
→ HVAC systems functions as:- Heating : which maintains your space / room warm during cold season or weather. The system uses a furnace or heat pump to warm air. The heat is generated through electric coils, gas, or oil and then circulated through ducts.
- Ventilation : which brings fresh air into your room / space while removing the stale air. It also maintain good indoor air quality by controlling humidity and reducing pollutants
- Air Conditioning (Cooling): Cools your room / space during hot season or weather. The air conditioning unit cools the air by removing heat through refrigeration cycles. Cooled air is distributed via ducts.
The importance of HVAC system in the operation of a hotel are:
- For Ensuring Guest Comfort: Ensures a comfortable temperature and air quality in rooms and public areas, which mainly enhances the guest satisfaction.
- Maintained Air Quality: Maintains clean, fresh air, which is very important for guest health and safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern HVAC systems reduce energy consumption, lowering operational costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Keeps various hotel facilities (kitchens, laundry rooms, gyms) running smoothly by regulating temperature and ventilation.
- Humidity Control: Prevents mold and mildew, maintaining a clean and safe environment.
- Compare between different forms of fuel to find out which one is most appropriate to be used in a hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Fuel)
→ The comparison of different forms of fuel are done below:
| Types of fuel | Heat Output | Cleanness | Smoke emission | Calorific Value | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kerosene | Good | Fairly clean | little | 11,100 kcal/kg | costly and restricted availability |
| Diesel Oil | Good | Fairly clean | little | 10,800 kcal/kg | costly |
| Coal gas | very good | very good | smokeless | 4,900 kcal/m3 | costly |
| Natural gas | Excellent | clean | smokeless | 9,500 kcal/m3 | less costly |
| Electricity | very good | cleanest | no smoke at all | costless | |
| LPG | very good | very clean | smokeless | 27,800 kcl/m3 | very costly |
| Solar energy | Low to moderate (Varies by system) | very clean | smokeless | High initial, Low ongoing |
Most appropriate to be use in a hotel are:
- Natural Gas is typically the most appropriate for hotel use due to its cost-effectiveness, relatively low environmental impact compared to other fossil fuels, and wide availability for heating, cooking, and water heating systems.
- Electricity is also widely used, especially when sourced from renewable energy, as it’s versatile and can power most hotel systems.
- Solar Energy is increasingly popular for hotels focusing to reduce their carbon footprint, though it requires significant upfront investment.
- What are the benefits of escalator and escalator system in a building. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Vertical transportation)
→ The benefits of escalator an escalator system in a building are:- Efficient Vertical Transportation: Escalators allow continuous movement of people between floors without waiting, reducing congestion.
- High Capacity: Can handle large numbers of people simultaneously, ideal for busy buildings like hotels, malls, and airports.
- Accessibility: Provides easy access for elderly, disabled, or people carrying heavy luggage, improving convenience.
- Space-Saving: Escalators take up less space compared to elevators, making them more suitable for high-traffic areas.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern escalator systems come with energy-saving features like sensors that slow down when not in use.
- Safety Features: Equipped with handrails, emergency stop buttons, and step safety features, ensuring user safety.
- Smooth Traffic Flow: Helps in controlling and directing the flow of people, improving overall building efficiency.
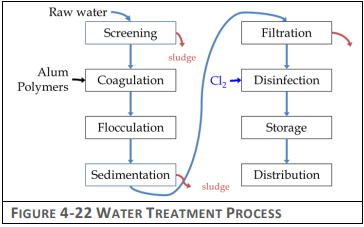
- Explain how water treatment plants works. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ The water treatment plants works on following steps:- Collection: Water is sourced from natural sources like rivers, lakes, or groundwater and directed into the treatment plant.
- Screening: Large debris like leaves, branches, and rubbish are removed using mesh screens.
- Coagulation and Flocculation: Chemicals (coagulants) are added to the water to bind small particles together, forming larger particles called flocs.
- Sedimentation: The water is then moved to sedimentation tanks where the heavy flocs settle at the bottom, allowing clearer water to move on.
- Filtration: The water passes through layers of sand, gravel, and charcoal to remove smaller particles and impurities.
- Disinfection: Chemicals like chlorine or UV light are used to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
- pH Adjustment: Sometimes, chemicals are added to adjust the water’s pH levels to make it less corrosive and safer for distribution.
- Storage: The treated water is stored in large tanks, ready for distribution to homes, hotels, and other facilities.
- Distribution: The clean, treated water is pumped through pipes to consumers, ensuring safe and clean drinking water.
- Explain Fire Classes and different types of fire production systems. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The classes of fire are:
| Category in the USA | Category in the UK / Europe | Fuel / Source of Fire | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Class A | Ordinary Combustibles | Wood, paper, cloth, plastics, rubber |
| Class B | Class B | Flammable liquids | Gasoline, oil, alcohol, paint thinner, kerosene |
| Class C | Flammable gases | Propane, butane, methane, hydrogen. | |
| Class C | Class E | Electrical equipment | Energized electrical appliances, wiring |
| Class D | Class D | Combustible metals | Magnesium, titanium, aluminum, sodium |
| Class K | Class F | Cooking oil or Fat | Cooking oils, grease, animal fats |
The types of fire protection systems are:
- Fire Extinguishers: Portable devices used for small, localized fires. Different types include:
- Water extinguishers (for Class A).
- CO2 extinguishers (for Class B and C).
- Dry chemical extinguishers (for Class A, B, and C).
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: Automatically activate when heat is detected, spraying water to extinguish or control fire spread.
- Fire Alarms: Detect smoke, heat, or flames and alert occupants through alarms and emergency signals, helping in evacuation.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Use chemicals, gases, or foam to suppress fires, often used in areas where water could cause damage (e.g., electrical rooms).
- Smoke Detectors: Detect smoke particles in the air and trigger alarms, helping in early fire detection and evacuation.
- Fire Blankets: Used to smother small fires, especially in kitchens or areas where flammable liquids are involved.
- Write TEN electrical safety precautions to be observed in a hotel. Calculate the monthly electrical bill of a household when the family uses following appliances with the corresponding duration of time in a day. Rate of electricity is Rs 12 per unit (KW.hr) (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
| No of appliances | Description of appliances | Operating duration in a day |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1500 watt geyser | 1 hour and 30 minutes |
| 8 | 25 watt CFL bulb | 8 hours |
| 1 | 50 watt TV | 15 hours |
| 1 | 150 watt single phase water pump | 1 hour |
→ The ten electrical safety precautions to be observed in a hotel are:
- One should always be careful and should not be distrated while working with electrical equipment.
- One should not energize any conductor immediately after any repair work is complete unless one is sure that everything is clear and there is none working on the conductor.
- The plug should not be disconnected by pulling the flexible cable off the socket.
- Before doing any work or replacing parts, always remember to put the main switch ‘off’.
- Safety demands good earthing. Hence, earth connection should always be kept in a good condition.
- While moving electrical appliances, such as table fan, iron, heaters, etc. one should be sure that these are disconnected from the electric supply. Switching off is not enough, as leaky insulations may give serious shocks.
- Live wires should always be connected through the switch.
- In case of electrical fire, one should not pour water on fire as it is dangerous.
- All fire extinguishes cannot be used for electrical fire; only CO2 extinguishers are used for this purpose.
- The hands should not be wet while handling electrical appliances.
- One should wear rubber-sole footwear while handling electrical appliances.
Solution:
| Items | Number | Power Consumption (kWh) | Duration (In hours) | Daily Energy Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geyser | 1 | 1.5 | 1 + 0.5 = 1.5 | 2.25 |
| CFL Bulb | 8 | 0.025 | 8 | 1.6 |
| TV | 1 | 0.05 | 15 | 0.75 |
| Water Pump | 1 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.15 |
| Total | 4.75 units |
Monthly Bill Calculation = 57 * 30 = Rs.1710
Solved Answer of Year 2019
- What are different types of loads that should be considered while designing a building? (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ The different types of loads that should be considered while designing a building are:- Dead Load – Permanent loads from the building structure itself (e.g., walls, floors).
- Live Load – Temporary or moveable loads (e.g., people, furniture).
- Define landscaping. (Unit 2: Design & Planning)
→ Landscaping refers to the planning, designing, and arranging of outdoor areas around a building, including elements like plants, trees, pathways, and water features to enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the environment. - What is hard cost? (Unit 3: Hotel Building Economic)
→ Hard costs are the direct expenses related to the physical construction of a building, such as materials, labor, equipment, and land development. These are tangible costs that are essential for the completion of the project. - Mention any four importance of conservation. (Unit 6: Conservation)
→ Any four importance of conservation are:- Preservation of Natural Resources – Ensures the sustainability of important resources like water, energy, and raw materials.
- Environmental Protection – Helps in reducing pollution and conserving ecosystems.
- Cost Savings – Reducing resource usage lowers operational expenses over time.
- Sustainable Development – Ensures that future generations can meet their needs without depleting resources.
- Briefly write on earthing of electrical system. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ Earthing, or grounding, refers to connecting the electrical system to the ground to ensure safety by preventing electrical shock. It provides a path for fault currents to flow directly to the earth, protecting both people and equipment from electrical hazards. - What are different types of water. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ The different types of water are:
On the basis of usage and treatment:- Potable Water – Safe for drinking and consumption.
- Grey Water – Reusable wastewater from sinks, showers, and washing machines.
- Black Water – Wastewater from toilets and kitchen drains that contains contaminants.
- Storm Water – Water collected from rainfall or runoff.
On the basis of mineral content:- Soft Water: Has a low concentration of minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium. It is often naturally occurring in areas with non-calcareous rocks or can be treated to remove hardness.
- Hard Water: Contains high levels of dissolved minerals, mainly calcium and magnesium. It is typically found in areas with limestone or chalk deposits.
- Write the full form of LED. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heat & Light)
→ The full form of LED is ‘Light Emitting Diode’. - List out the different types of protective device. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The different types of protective device are:- Fuse
- Circuit Breaker
- Surge Protector
- Residual Current Device (RCD)
- Lightning Arrester
- Define COP. (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ COP, or Coefficient of Performance, is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigeration system. It is the ratio of the amount of cooling or heating provided to the energy input, with higher COP indicating a more efficient system. - Point out the different modes of vertical transportation in a hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Vertical Transportation)
→ The different modes of vertical transportation in a hotel are:- Elevators – For transporting guests and staff between floors.
- Escalators – Moving staircases for continuous transport between floors.
- Staircases – Traditional manual form of vertical transport.
- Dumbwaiters – Small elevators used for moving goods or food between floors.
- Explain in detail about the different types of building structures based on the constructions methods. (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ The different types of building structures based on the construction methods are:- Load-Bearing Structure: In this method, the walls bear the load of the structure and transfer it to the foundation. It is one of the oldest construction methods and typically involves masonry walls.
Materials: Brick, stone, or concrete blocks.
Applications: Common in small residential buildings or traditional constructions.
Advantages: Simple to build, low cost for small structures.
Disadvantages: Limited height of the structure due to weight distribution on the walls. - Framed Structure: A skeleton frame of columns and beams supports the building’s load. The walls are non-load bearing, and the load is transferred to the foundation through the frame.
Applications: High-rise buildings, commercial spaces, modern residential buildings.
Advantages: Flexible layout, can support larger heights and wider spans.
Disadvantages: Higher cost and complexity in construction.
Types:
a. Steel frame: Uses steel beams and columns.
b. Concrete frame: Uses reinforced concrete.
- Load-Bearing Structure: In this method, the walls bear the load of the structure and transfer it to the foundation. It is one of the oldest construction methods and typically involves masonry walls.
- What are the different types of Guestroom Floor Configuration in a hotel? (Unit 2: Design & Planning)
→ - Sketch the open and closed circuit describing its function. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ - Explain the Cooling system of hotels with necessary sketch. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heating, ventilation and Air conditioning)
→ - Describe the major element of fire and also explain about its classification. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The major elements of fire are:
a. Oxygen
b. Fuel
c. Heat
d. Chemical Chain Reaction
| Category in the USA | Category in the UK / Europe | Fuel / Source of Fire | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Class A | Ordinary Combustibles | Wood, paper, cloth, plastics, rubber |
| Class B | Class B | Flammable liquids | Gasoline, oil, alcohol, paint thinner, kerosene |
| Class C | Flammable gases | Propane, butane, methane, hydrogen. | |
| Class C | Class E | Electrical equipment | Energized electrical appliances, wiring |
| Class D | Class D | Combustible metals | Magnesium, titanium, aluminum, sodium |
| Class K | Class F | Cooking oil or Fat | Cooking oils, grease, animal fats |
- What is building cost and building structure cost? (Unit 3: Hotel Building Economic)
→ - What are the process taken under consideration before taking the decision for the new source of water and if it is feasible enough, how are the impurities removed from the raw water to make it potable? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ - Activities of maintenance functions could be either repair or replacement activities which are necessary for an item to reach its acceptable productivity condition or these activities should be carried out with a minimum possible cost, so what are the importance of maintenance?
Also further explain the maintenance management system. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Maintenance)
→ Importance of maintenance is repeated from Year 2018 Question Number 11 (Please refer back to that year for answer)
Solved Answer of Year 2021
- Explain Waste Management of 5 star Hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ - Prepare an organizational chart of Facility Department. Also write major duties and responsibilities of chief engineer. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Engineering department)
→ An organizational chart of facility department is shown below:
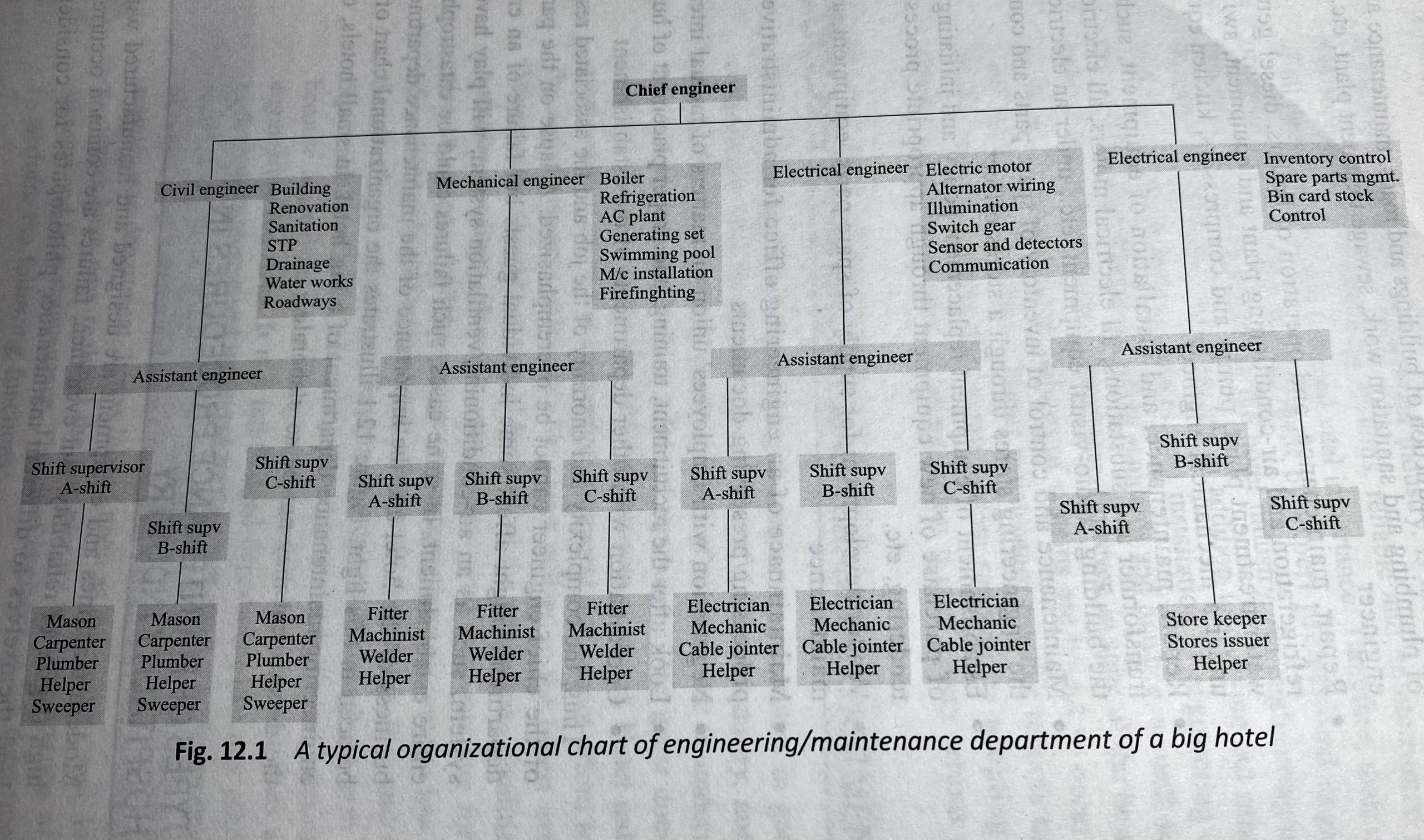
The major duties and responsibilities of chief engineer are:
- Overseeing the operation:
- Manage and coordinate the facility department, ensuring smooth operation of electrical, plumbing, HVAC, and mechanical systems.
- Maintenance Management:
- Ensure regular preventive maintenance schedules for all critical systems to avoid breakdowns.
- Supervise maintenance tasks and provide support during emergencies.
- Budgeting and Cost Control:
- Prepare maintenance and repair budgets, allocate resources effectively, and control costs without compromising on service quality.
- Compliance and Safety:
- Ensure the facility complies with local safety regulations, building codes, and health and safety standards.
- Implement safety measures and conduct regular inspections to prevent accidents and equipment failures.
- Energy Management:
- Implement energy-saving strategies to reduce utility consumption and operational costs.
- Oversee the efficient use of energy and resources in the building.
- Team Leadership:
- Lead, train, and manage the facility team, including technicians, electricians, plumbers, and maintenance staff.
- Conduct regular performance reviews and provide ongoing training to the team.
- Vendor Management:
- Coordinate with external vendors for the procurement of parts, services, and maintenance contracts.
- Ensure the timely repair and replacement of equipment through external contractors when necessary.
- Crisis Management:
- Respond to facility emergencies, such as power outages, plumbing issues, and mechanical failures, ensuring quick resolutions.
- Project Management:
- Responsible for supervise renovation and construction projects within the hotel or facility, ensuring timely completion within budget and as per the plan.
- Explain the elements of fire. Also, explain Fire classes. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ Repeated question from Year 2019, Qn no.15 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Sketch Refrigeration Cycle. Also, write the main function of each component. (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ - Sketch a typical guest room with Fixtures and Furniture. (Unit 2: Design & Planning)
→ - Find the current passing through 3 Hp pump motor having 0.8 Power factor connected across 230V. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ Solution
We know the formula,
| P = V * I * Power factor |
P = Power in watts (W)
V = Voltage in volts (V)
I = Current in amperes (A)
Converting horsepower into watts
| 1 Hp = 746 |
3Hp = 3 * 746 = 2238 W
Using the formula,
P = V * I * Power factor
or, 2238 = 230 * I * 0.8
or, 2238 = 184 I
or, 2238 / 184 = I
∴ I = 12.16A
Thus, the current passing through the 3 HP pump motor is approximately 12.15 A.
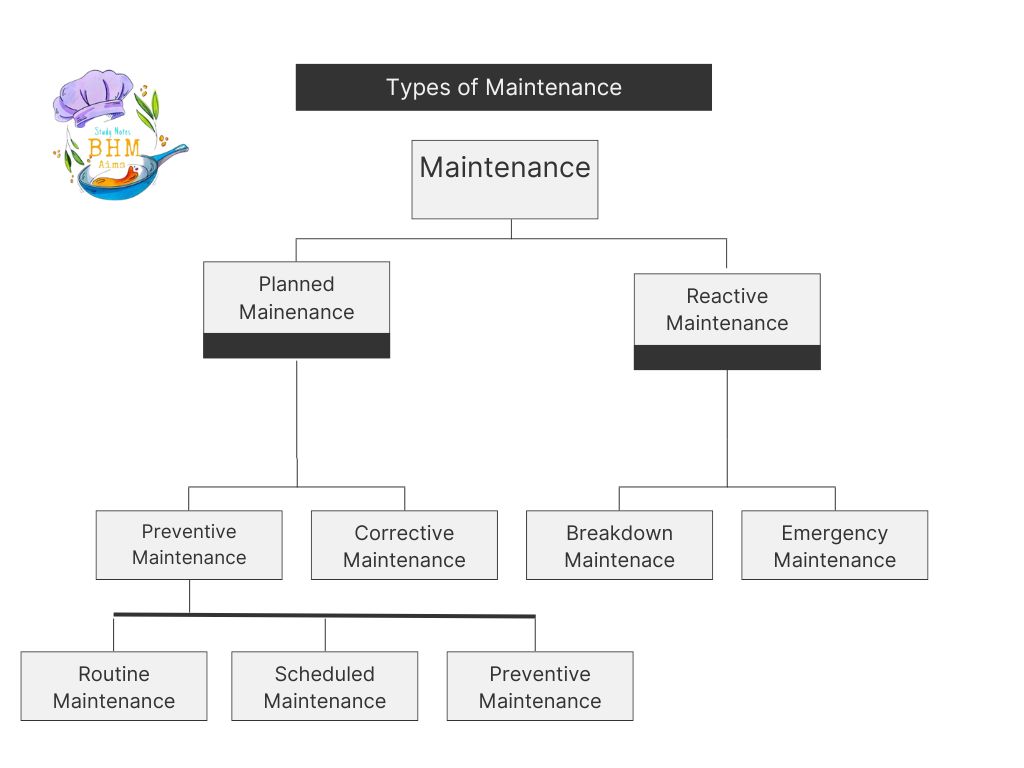
- Discuss all types of maintenance. Also, discuss the relationship between the Facility Department and the other departments of a hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Maintenance)
→ The types of maintenance are shown in below figure:
- Discuss usages, sources, analysis and impurities of Water in a 5 star hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→
Solved Answer of Year 2022
- Define “One Volt”. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ One volt is the unit of electric potential difference or electromotive force. It is defined as the amount of electric potential required to move one coulomb of charge through a conductor with one joule of energy.
Mathematically,
1 Volt (V)=1 Joule (J)/1 Coulomb (C) - What is the main cause to block the water pipe? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ The causes to block the water pipe The main cause of water pipe blockages is the accumulation of debris, such as mineral deposits (scaling), grease, hair, dirt, and sediments, or the intrusion of roots into the pipe system.
(OR)
You can also write:
- Mineral Deposits (Scaling) – Buildup of calcium and magnesium from hard water.
- Grease and Oil – Fats and oils solidify inside pipes, causing blockages.
- Hair – Accumulates in pipes, especially in bathroom drains, leading to clogs.
- Dirt and Debris – Sand, dirt, or other particles from water supply or external sources.
- Soap Scum – Residue from soap can mix with minerals in the water and form clogs.
- Corrosion – Rust or corrosion inside old metal pipes reduces the pipe diameter.
- Foreign Objects – Items like sanitary products, wipes, or other non-flushable objects.
- Tree Root Intrusion – Roots from trees can grow into underground pipes, blocking water flow.
- Food Waste – Particularly in kitchen drains, food particles can build up over time.
- Small Animal Intrusion – In some cases, rodents or insects can obstruct pipes.
- Define High Rise Building. (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ A high-rise building is generally defined as a tall structure with multiple floors that exceeds a certain height, requiring specific architectural and engineering considerations for its design, safety, and functionality. - What do you mean by building economics? (Unit 3: Hotel Building Economic)
→ Building economics refers to the study and management of the costs associated with the construction, maintenance, and operation of a building. - Define “Deep Foundation”. (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ A deep foundation is a type of foundation used for transferring building loads to deeper layers of soil or rock that are more stable, especially when surface soils are weak or unstable. Examples include pile foundations and drilled shafts. - Write the meaning of “Two-way switch”. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ A two-way switch is a type of electrical switch that allows control of a single light or electrical device from two different locations, commonly used in staircases or large rooms. - Write three examples of Class “A” Fire. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Safety & Securities)
→ The three examples of class “A” fire are:
Class ‘A’ are common combustible materials that Class “A” fires involve.- Wood
- Paper
- Cloth
- What do you mean by Ventilation System? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heating, ventilation and Air conditioning)
→ A ventilation system is designed to provide fresh air to an indoor space by removing stale air and introducing outdoor air. It helps maintain indoor air quality, controls humidity, and prevents the buildup of pollutants. - What is the main function of MCB? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ The main function of a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overloads or short circuits by automatically switching off the electrical flow when excessive current is detected. - What is “Heat”? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heat & Light)
→ Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between objects with different temperatures. It flows from the hotter object to the cooler one, and it can be produced through various processes such as combustion, friction, or electrical resistance. - Describe on waste management of a five-star hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→ - Prepare the responsibilities of the head of Facility Department. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Engineering department)
→ The head of facility department is ‘Chief engineer’. The roles and responsibilities of him / her are:
Repeated question from Year 2021, Qn no 2 (Please refer back to that year for answer) - Explain the causes of fire and its precautions. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ - What is HVAC? Explain. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heating, ventilation and Air conditioning)
→ - Sketch kitchen layout with fixtures and furnitures. (Unit 2: Design & Planning)
→ - Find the current passing through 5HP pump motor having 0.85 power factor connected across 220V. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ Solution
We know,
1Hp = 746 watt
Given,
Power = 5Hp = 746 * 5 = 3730 watt
Power factor = 0.85
Voltage (V) = 220V
Now,
| Current (I) = Power (W) / (Voltage * Power Factor) |
= 3730 / 187
= 19.95 A
Result: The current is approximately 19.05 ampere.
- Define “Maintenance”. Discuss all types of maintenance and the relationship between the Facility Department and other departments of a hotel. [1+5+4] (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Maintenance / Engineering department)
→ Maintenance is the systematic process of ensuring that equipment, systems, buildings, and other assets are kept in optimal working condition through regular inspections, repairs, adjustments, and preventive measures. It involves a series of activities aimed at preserving the functionality, safety, and efficiency of the assets over their lifespan.
The types of maintenance is shown below:

- Define the term quality of water. Discuss about the water treatment plant in a hotel. [2+8] (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Water and waste water system)
→
Solved Answer of Year 2023
- Name the components of structure. (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ The components of structure are:- Foundation
- Plinth
- Columns
- Beams
- Walls
- Lintels
- Damp Proof Course (DPC)
- Mention the type of parking according to service. (Unit 2: Design and planning)
The type of parking according to service are:- Self-parking – Guests park their vehicles themselves in designated spots.
- Valet parking – A valet attendant parks the vehicles for guests.
- Automated parking – Mechanical systems or machines park the vehicles automatically.
- List down the steps to extinguish fire. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The steps to extinguish fire are:- Evaluate the fire – Determine the size and type of fire.
- Pull the alarm – Notify others and call emergency services.
- Use the correct fire extinguisher – Choose the extinguisher suited for the class of fire (e.g., water for Class A, CO2 for Class B).
- Aim at the base of the fire – Direct the extinguisher nozzle at the fire’s base.
- Sweep the extinguisher – Move the extinguisher side to side to cover the entire area.
- Evacuate if necessary – If the fire grows or becomes uncontrollable, evacuate immediately.
- Define capital project cost. (Unit 3: Hotel Building Economic)
→ Capital project cost refers to the total expenditure required for the construction, renovation, or major maintenance of a building, including expenses related to land acquisition, materials, labor, equipment, design, and permits. It includes all costs necessary to complete and operate the project. - When will short circuits occur in a circuit? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ A short circuit occurs when electrical current flows through an unintended path of low resistance, bypassing the normal circuit. This usually happens due to faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or direct contact between live wires, resulting in a surge of current that can cause overheating and potential fire hazards. - How do you explain electromagnetic wave? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
→ Electromagnetic waves are waves of energy that propagate through space, consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These waves travel at the speed of light and do not require a medium to move through. Examples include light, radio waves, and X-rays.
Simply, Electromagnetic waves are energy waves made up of electric and magnetic fields that move together - Explain British thermal unit. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heat & Light)
→ A British Thermal Unit (BTU) is a unit of measurement for energy. It represents the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is commonly used in heating and cooling systems to measure energy consumption or output. - Enlist two properties of good Refrigeration. (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ Any two properties of good refrigeration are:- Low boiling point – Ensures efficient heat absorption and cooling.
- Non-toxic and non-flammable – Ensures safety for use in refrigeration systems.
- Write down the full form of CCTV. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities)
→ The full form of CCTV is ‘Closed Circuit Television’. - Define coefficient of performance. (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ Repeated question from 2019, Qn No. 9 (Please refer back to that year) - A refrigerator extracts heat from foodstuffs at a capacity of 1.5 ton of refrigeration. The electric motor driving the compressor of the refrigeration unit consumes-power of 1.2 kw. Determine the COP of the unit. (Unit 5 : Food Service Refrigeration)
→ Solution
We know,
1 ton of refrigeration is equivalent to 3.517 kW.
Given,
Cooling capacity = 1.5 ton
= 1.5 * 3.517
= 5.2755 kW
Power input = 1.2kw
Now,
| COP = Cooling Capacity / Power Input |
COP = 5.2755 / 1.2
=4.39625
Therefore, Coefficient of Performance (COP) of the refrigeration unit is approximately 4.40.
- Explain in brief about different types of fire extinguishers. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Safety & Securities)
→ Each extinguisher is designed for specific types of fires, so it’s important to use the right one for the situation. The different types of fire extinguishers are:- Water Extinguishers (Class A): They are used for fires involving solid materials like wood, paper, and fabric. They work by cooling the fire and removing the heat.
- Foam Extinguishers (Class A & B): They are effective for fires involving flammable liquids like petrol and oils, as well as solid materials. Foam creates a barrier between the fire and the oxygen, smothering it.
- Dry Powder Extinguishers (Class A, B, C): They are suitable for fires caused by flammable gases, liquids, and electrical equipment. It works by smothering the fire, removing oxygen.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Extinguishers (Class B & Electrical): They are used for electrical fires and flammable liquid fires. CO2 extinguishers work by displacing oxygen and cooling the fire.
- Wet Chemical Extinguishers (Class F): They are designed for kitchen fires involving oils and fats, like deep-fat fryers. They cool and smother the fire, preventing it from re-igniting.
- Define protecting device. Explain why protecting device is necessary in circuit. How fuse is differing from Miniature Circuit Breaker? (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering -Safety & Securities and Electricity)
→ A protecting device is an electrical component designed to safeguard electrical circuits and equipment from damage due to faults, overloads, or other abnormal conditions. These devices interrupt the flow of electricity when a fault is detected, preventing potential damage and ensuring safety.
Protecting device is necessary in circuit because:- Prevent Damage: Avoids damage to circuits and equipment.
- Enhance Safety: Reduces risk of electrical fires and shocks.
- Minimize Downtime: Limits disruption to only affected areas.
- Compliance: Ensures adherence to safety standards.
- Prevent Overloading: Stops circuits from overheating.
The difference between fuse and Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) are:
| Basis | Fuse | MCB |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Melts and breaks the circuit when excessive current flows. | Automatically switches off and disconnects the circuit when an overload or short circuit occurs. |
| Resetting | Requires replacement of the fuse element once it blows. | Can be reset manually by switching it back on after it trips. |
| Response time | Generally slower in response compared to MCBs. | Responds quickly to overloads and short circuits. |
| Indicator | No visual indicator when it blows; must be checked. | Typically has a visible switch that indicates the tripped status. |
| Cost | Cheaper than MCB | Expensive than fuse, but durable |
| Use | Common in older installations and simple circuits. | Common in modern installations and more complex circuits. |
- Write down the difference between shallow foundation and deep foundation. (Unit 1: Physical plant and building)
→ The difference between shallow foundation and deep foundation are:
| Basis | Shallow foundation | Deep foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Typically extends less than 3 meters (10 feet) below ground level. | Extends much deeper, usually beyond 3 meters (10 feet). |
| Usage | Used for buildings with lighter loads and stable soil near the surface. | Used for heavy structures or when soil near the surface is unstable. |
| Types | Includes spread footings, strip footings, and mat foundations. | Includes piles, caissons, and drilled shafts. |
| Cost | Generally less expensive due to simpler construction. | More costly due to complex construction and materials. |
| Construction complexity | Simpler and quicker to construct. | More complex and time-consuming. |
| Loan Distribution | Distributes loads over a larger area near the surface. | Transfers loads to deeper, more stable soil or rock layers. |
| Suitability | Suitable for small to medium-sized buildings on stable soil. | Suitable for large buildings, bridges, and in areas with weak soil. |
| Installation | Installed directly on the ground or on a shallow base. | Requires drilling or driving piles deep into the ground. |
- What are the different modes of transfer of heat? Brief them. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Heat & Light)
→ - Describe about the maintenance management system of Hotel. (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Maintenance)
→ - Explain the five-safety precaution that must be adopted while using electronic appliances. Suppose a 3-star hotel is using these items: (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Electricity)
- 1000 number Of 25 watts bulbs for 4 hours and 45 minutes per day
- 300 units TV Of 200 watts average 12 hours per day
- Freeze & refrigeration 25 units of 150 watts 24 hours per day
- 7.5 hp electric pumps 3 hours and 30 minutes per day
- If electric tariff per KW hr, is Rs 10 per units, Calculate the monthly bill for the month Of July.
→ Solution
Considering, The total days count in July is 31.
We know,
1 hp = 0.746 kW
1 kW = 1000 W
| Items | Number | Power Consumption (kWh) | Duration (In hours) | Daily Energy Consumption (kWh) | Monthly Energy Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulb | 1000 | 0.025 | 4 + 0.75 = 4.75 | 118.75 | 3681.25 |
| TV | 300 | 0.2 | 12 | 720 | 22320 |
| Freeze & refrigeration | 25 | 0.15 | 24 | 90 | 2790 |
| Electric pumps | 1 | 5.6 (7.5 hp ≈ 5.6 kW) | 3 + 0.5 = 3.5 | 19.6 | 607.6 |
| Total | 949.35 units | 29,398.85 units |
The monthly electricity bill for the month of July is Rs 293,988.50.
Working Note:
Energy Consumption (kWh) = Number of bulbs × Power consumption per bulb × Duration
- Bulb: Units = 1000 bulbs × 0.025kWh × 4.75hours = 118.75 kWh
- TV Units=300 TVs × 0.2 kWh × 12 hours = 720 kWh
- Freeze & Refrigeration: Units = 25 units × 0.15 kWh × 24 hours=90 kWh
- Electric Pumps: Units = 1 pump × 5.6 kW × 3.5 hours = 19.6 kWh
| Total Units = 118.75+720+90+19.6=949.35 kWh |
- Discuss all types of maintenance. Also discuss the relationship of engineering department with (Unit 4: Hospitality Engineering – Engineering department)
- Kitchen Department
- FrontOffice
- Housekeeping Department
- Security Department
- Human Resource Department
→ Types of maintenance already answered in Year 2022 Question number 17 (Please check answer from that Year)
Practice Questions





