Table Of Contents
Past Question Paper
| Dear Students, If you find any question paper missing from any year, please contact us through our email address “bhmaims@gmail.com“ Also, if you have any missing past-year board question papers, kindly forward them to us so that we can update in our website. |
Economics Year 2017 Question Paper

Economics Year 2018 Question Paper

Economics Year 2019 Question Paper

Economics Year 2021 Question Paper

Economics Year 2022 Question Paper

Economics Year 2023 Question Paper

Solved Answer
Solution of Year 2017
- What is microeconomics?
→ Microeconomics, also known as Price Theory is defined as the study of behavior of individual decision making units, such as a consumer, a household, a firm. - List out the factors which cause shift in tourism supply curve.
→ The factors which cause shift in tourism supply curve are:
a. Government policies and regulations
b. Price of the commodity
c. Price of related goods
d. State of technology
e. Prices of input or cost of product - What are the composition of tourism products?
→ The composition of tourism products are:
a. Accommodation
b. Attractions
c. Transportation
d. Amenities and Services
e. Sales and Distributions (like tour operators, travel agencies, OTAs, etc.)
f. Infrastructure
g. Events and activities - What is tourism product?
→ A tourism product is a bundle of goods and services offered to travelers that creates a complete and satisfying travel experience.
(OR)
Tourism or tourist product can be defined as the sum of the physical and psychological satisfaction provided to tourists during their travel and stay at the destination. - Distinguish between scarce and free resources in tourism.
→ The differences between scarce and free resources in tourism.
| Basis | Scarce Resource | Free Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Limited in availability and often require management or conservation. | Being free doesn’t mean unlimited but abundant and typically available without cost. |
| Presence | less than its desired use | more than its desired use |
| Examples | Natural attractions (e.g., national parks), heritage sites, hotel rooms, and transportation services. Also, worker, equipment, raw materials, etc. | Natural resources like Scenic views, fresh air, and landscapes. Cultural resources like arts, traditions, etc. |
| Cost | Often associated with significant costs for usage or preservation. | Generally free of charge for public use. |
- Distinguish between fixed and variable cost.
→ The differences between fixed and variable cost are:
| Fixed Cost (FC) | Variable Cost (VC) |
|---|---|
| FC are incurred on the fixed factors of productions like machines, buildings, insurance, etc. | VC are incurred on variable factors of production like Labour, raw materials, transport, etc. |
| FC do not increase or decrease with a rise or fall in the level of output. | VC changes with changes in the level of output. |
| FC cannot be changed during short-run. | VC can be changed during short-run. |
| FC are never zero even when production is stopped. | VC are zero when production is stopped. |
| Production at the loss of FC may continue. | Production at the loss of VC will not continue. |
| Graphically, TFC curve is parallel to x-axis. | Graphically, TVC curve is inverse S-shaped |
- Prepare the list of determinants of leisure and tourism.
→ A list of determinants of leisure and tourism are:
a. Economic Factors: Income levels, employment rates, and overall economic conditions influence travel spending and patterns.
b. Social and Cultural Factors: Social trends, cultural preferences, and lifestyle choices affect travel behavior and destination selection.
c. Political Factors: Government stability, visa regulations, and travel policies can impact tourism flow and destination appeal.
d. Technological Factors: Advances in technology, such as online booking systems and travel apps, facilitate and influence travel planning.
e. Marketing and Promotion: Advertising, promotional campaigns, and destination branding influence tourists’ awareness and interest in various locations.
f. Infrastructure and Accessibility: Quality of transportation, accommodation, and other facilities determines ease of travel and overall destination attractiveness.
Others determinants like: Health and safety, environmental factors, personal preferences, seasonality, geographical factors, etc. - What are the conditions of price discrimination?
→ The conditions of price discrimination are:
a. Market Power or Monopoly: The seller must have the ability to influence prices, typically by having some level of control over the market.
b. Market Sealing: The markets for different classes of consumers are so separated that buyers of low-price market do not find it profitable to resell the commodity in the high-price market. The factor that separate markets include are: (i) geographical distance involving high cost of transportation (ii) exclusive use of the commodity example: doctor’s services, entertainment shows, etc. and (iii) lack of distribution channels e.g. transfer of electricity and gas
c. Market Segmentation: The seller must be able to segment the market into distinct groups based on characteristics such as age, location, or purchase behavior.
d. Different elasticity of demand: If market is divided into sub-market, the elasticity of demand at a given price must be different in each sub-market. If price elasticities of demand in different rare the same, price discrimination would not be gainful. only the difference in price elasticities that provides opportunity for price discrimination - Write any four causes of inflation.
→ The four causes of inflation are:
a. Increase in money supply (Falls under Demand Pull Inflation)
b. Reduction in taxes (Falls under Demand Pull Inflation)
c. Increase in wage rate (Falls under Cost Push Inflation)
d. Increase in interest rate (Falls under Cost Push Inflation) - Prepare the list of characteristics of monopoly.
→ A list of characteristics of monopoly are:
a. Single Seller: One company or entity controls the entire market for a product or service.
b. Profit Maximizer: The monopolist aims to maximize profits by adjusting output and pricing.
c. Price Maker: The monopolist has the power to set prices rather than accepting market prices.
d. Strong Barriers to Entry: High barriers prevent other firms from entering the market, such as high startup costs, legal restrictions, or control of essential resources.
e. Price Discrimination: The monopolist may charge different prices to different consumers based on their willingness to pay. - Why tourism industry needs economic analysis? Explain the types of economic analysis.
→ Comprehensive study of economics condition, activities, behavior of organization, identification of problems, causes, effect of economic problem is simply known as economic analysis. An economic analysis is a process in which business owners gain a clear picture of the existing economic climate, as it relates to their company’s ability to thrive or sustain. These types of economic evaluation consist of an in-depth appraisal of the strengths and weakness of the market.
Economic analysis is crucial for the tourism industry because it helps stakeholders understand the economic impact, forecast future trends, and make informed decisions. Here’s why economic analysis is essential in tourism:
- Understanding Economic Impact
- Direct and Indirect Contributions: Tourism generates income through direct spending on hotels, restaurants, and attractions. It also has indirect effects, such as supporting industries (e.g., transportation, food suppliers). Economic analysis quantifies these impacts.
- Employment: Tourism is a major source of employment. Analyzing its economic impact helps determine job creation and income generation across different regions.
- Resource Allocation:
- Investment Decisions: Economic analysis guides governments and private sectors in allocating resources, such as infrastructure development, marketing, and tourism services. It helps prioritize investments that yield the highest returns.
- Budget Planning: Governments use economic analysis to plan budgets, allocate funds, and set tax policies related to tourism. This ensures that public funds are used efficiently to boost tourism growth.
- Sustainability and Policy Formulation:
- Environmental and Social Costs: Tourism can lead to environmental degradation and social challenges. Economic analysis helps assess these costs and develop sustainable tourism policies that balance growth with conservation.
- Policy Development: Economic analysis aids in developing policies that optimize tourism benefits while minimizing negative impacts, such as overcrowding or cultural degradation.
- Forecasting and Strategic Planning:
- Trend Analysis: By analyzing economic indicators, such as GDP contribution, tourist arrivals, and spending patterns, stakeholders can forecast future trends and adapt strategies accordingly.
- Crisis Management: Economic analysis helps anticipate the impact of crises (e.g., pandemics, economic downturns) on tourism and devise strategies to mitigate these effects.
- Regional Development:
- Balanced Growth: Economic analysis highlights the regional disparities in tourism development, guiding efforts to promote balanced growth across different areas, especially in underdeveloped or rural regions.
The types of economic analysis are:
- Cost analysis: The estimation of overall cost of land, labour, capital, raw material, energy of project is known as cost analysis.
- Budget analysis: The estimation of total budget to implement the project is budget analysis.
Following are the major that includes in economic analysis:
- Cost – Benefit Analysis
- Cost – Effective Analysis
- Cost – Minimization Analysis
- How is equilibrium price determine under perfect competition? In which conditions there is surplus and shortages?
→ - Explain the factors that affect travel and tourism yields and future.
→ - What is tourism demand forecasting? How tourism Demand forecasted using time series model?
→ - Explain the interrelationships between tourism and others sectors of economy.
→ The success of tourism industries depends upon the relationship between among the industries and other sector of the economy. The following points are used to show the interrelationship.
- Tourism and agriculture sector: Tourism and agriculture sector are positively related. For example, agricultural sectors produced chicken, pork, mutton, beef, buff and fruits, veritable, foodstuffs used by hotels, restaurants to serve the tourists. Hotels, restaurants, travel agency provides good prices in the exchange for goods and service, employment opportunities to the farmers, peasants at theirs leisure time. Farm house accommodation and agriculture tourism termed as a means of boosting income particularly at the offseason. Similarly tourist also get healthier lifestyle, natural food and outdoor life. In this way there is a forward and back ward linkage between tourism and agriculture.
- Tourism and Business sector: In tourism there is a distribution path. The term ‘distribution path’ refers to the path or route that a product takes in order to move from the original producer or supplier (principal) to the person who will use it. In the tourism industry various businesses from different sectors work together so that a service (eg. air travel) is made available to a potential tourist. For example, an airline could sell its services directly to the consumer via telephone bookings to its reservation centre or through its own travel agency (e.g. Qantas Travel Centre). The airline could also sell its services through travel agencies (eg Harvey World Travel) or by including its services with a tour wholesaler’s package. (e.g. Qantas Holidays). The wholesaler might then sell this package directly to the consumer or also via a travel agency. The travel agency might sell directly or through the agent. In this way there is a different path of business.
- Tourism and Industries: Industry sectors not only work together to provide a package of services and to distribute a particular product, but also work together to promote tourism services. This is called cooperative advertising or promotion. For example, a local tourist attraction, motel and small regional tour operator may jointly pay for space at a trade show or consumer show (eg Holiday and Travel Show) to promote their individual services.
- Tourism and Sport Science & research sector: There is a positive and significant relationship between tourism and sports science and research to each other. Tourism linking can be highlight the interrelationships among the Tourism industry sectors needed to provide a package of services for a potential tourist: A person in the tourism generating Lumbini (home country, town or region) sees an Lumbini Television (promotion and distribution sector) for a holiday package (tour operator and wholesaler sector) with travel by Buddha Airways (transportation sector) staying at the Buddha Hotel (accommodation sector) in Lumbini with an escort around Lumbini sights (industry services sector) and major attractions including Maya devi temple, Ashoka pillar and Lumbini Harbour museum. The advertisement recommends using an ZIYA Travel Agent (coordination sector) and that for each booking, discount shopping vouchers will be provided (retail services sector). Another example may be purchasing a relaxing holiday to Heron Island, Queensland where they conduct research of the Great Barrier Reef and now even include tourists helping to monitor the health of the reef. Not only that they are also involved in conserving the vulnerable turtle species that use Heron as their breeding ground.
- Tourism and Arts Cultures and Entertainment: It is crucial and positive relationship between art, culture and tourism. The heritage artistic and cultural life an area can adopt tourist and create the better quality of life for those who live in there. A city or town with the drives cultures option and attraction like museum, opera, art galleries, theaters are the attractions not only to their resident but also for a visitor. Because tourist can discover more and more memorable experience. Learning new culture, tradition, language and enjoying more beautiful time. One example you may be purchasing an overnight package with an accommodation (home-stay at Bandipur, Nepal) that includes entry into a show or sporting event (cultural art/ entertainment/sports) including dinner/breakfast and maybe even transportation facilities.
- Hotel Tourism and Local Resources: Tourism and local resources utilization as positive and direct relationship. The development of the the country depends on more efficient utilization of local resources and greater local participation in the industry in general.
- (a) The source of local supplies to hotels, ie. whether small or large farms; The restaurants of Sauraha of chitwan district have much wider verity of chicken and eggs than Kathmandu. More yak milk and cheess offer in khumbu area of Solukhumbu and many other areas resturent offer locally grown food.
- (b) The marketing and distribution systems involved in the present movement of local agricultural supplies to the hotels, are generally local women groups, agriculture cooperative, youth clubs, etc. play important role in Nepal.
(Or, For more easy points you can also choose any 5 points from below)
- Hospitality and Accommodation Sector
Interrelationship: Tourism directly drives demand for accommodation, including hotels, resorts, guesthouses, and other lodging facilities. As more tourists visit a destination, the need for places to stay increases, benefiting the hospitality sector.
Impact: Revenue generated from accommodation services contributes to the local economy. It also creates jobs, ranging from housekeeping to management roles, and stimulates investment in new hospitality infrastructure. - Transportation Sector
Interrelationship: Tourism relies heavily on transportation, including air travel, railways, road transport, and maritime services. Tourists need transportation to reach their destinations and move around once they arrive.
Impact: Increased tourism boosts demand for transportation services, leading to higher revenues for airlines, bus companies, car rental services, and more. This also encourages investments in transportation infrastructure, such as airports, roads, and ports. - Food and Beverage Industry
Interrelationship: The food and beverage (F&B) sector benefits from tourism as tourists spend on dining, whether in restaurants, cafes, bars, or local food stalls. This relationship is particularly strong in destinations known for their culinary offerings.
Impact: Tourism drives growth in the F&B industry, leading to the creation of new restaurants, cafes, and bars, as well as jobs for chefs, waitstaff, and other hospitality professionals. It also stimulates demand for locally sourced food products, benefiting farmers and suppliers. - Retail and Handicrafts Sector
Interrelationship: Tourists often engage in shopping for souvenirs, clothing, and other goods, which supports the retail sector. Handicrafts, in particular, are popular purchases, representing local culture and traditions.
Impact: Increased tourist spending in retail boosts sales, generates revenue, and supports local artisans and small businesses. This sector often provides employment opportunities, especially in regions where traditional crafts are a significant part of the economy. - Cultural and Entertainment Sector
Interrelationship: Tourism is closely linked to cultural attractions and entertainment, including museums, theaters, festivals, and heritage sites. These attractions draw visitors and provide cultural experiences that enhance their travel.
Impact: The tourism-driven demand for cultural and entertainment experiences supports the preservation of heritage sites and the arts. It also creates jobs for artists, performers, guides, and other professionals in the cultural sector. - Agriculture and Food Production
Interrelationship: Tourism influences agriculture by creating demand for food products, especially in regions where farm-to-table dining and agritourism are popular. Local agriculture can also be a part of the tourist experience, such as through vineyard tours or farm visits.
Impact: The demand from the tourism sector can lead to increased agricultural production and diversification. It also provides farmers with additional income streams through direct sales to hotels and restaurants or through agritourism activities. - Construction and Real Estate
Interrelationship: Tourism stimulates construction and real estate development, including the building of hotels, resorts, vacation homes, and entertainment facilities. Infrastructure development, such as airports and roads, also falls within this sector.
Impact: The growth in tourism leads to increased demand for construction services and real estate, boosting the local economy. It creates jobs in construction, architecture, and real estate management. Moreover, property values in tourist areas often rise, benefiting property owners and investors. - Financial Services
Interrelationship: Tourism generates a need for financial services, including currency exchange, banking, insurance, and investment in tourism-related projects. Tourists and businesses involved in tourism often require these services.
Impact: The financial sector benefits from the increased transactions and investments driven by tourism. This includes more business for banks, higher demand for insurance products, and opportunities for investment in tourism infrastructure and services. - Environmental Management and Conservation
Interrelationship: Tourism, especially eco-tourism, is connected to environmental conservation efforts. Sustainable tourism practices encourage the protection of natural resources and biodiversity, which are often key attractions for tourists.
Impact: The relationship between tourism and the environment leads to investments in conservation projects and environmental management. Tourism can fund the maintenance of national parks, protected areas, and wildlife conservation programs. - Healthcare Sector
Interrelationship: Tourists may require healthcare services, especially in cases of medical tourism where individuals travel specifically for medical procedures or wellness treatments.
Impact: The healthcare sector benefits from the influx of medical tourists, leading to higher demand for healthcare services and facilities. This can result in job creation and improved healthcare infrastructure, benefiting both tourists and local residents. - Education and Training
Interrelationship: The tourism industry requires a skilled workforce, which drives demand for education and training programs in hospitality, tourism management, and languages. Educational institutions often offer specialized courses and degrees in these areas.
Impact: The need for a qualified workforce leads to the growth of educational programs and institutions focused on tourism-related fields. This also enhances the skills of the local population, leading to better job opportunities and career advancement within the tourism industry.
- Discuss the challenges for the supply of tourism product.
→ - Explain the versions degree of price elasticity of tourism demand. If income of the tourist increase from 4000 to 5000 the quantity demand of tourism product increase from 10 units to 40 units. Compute the income elasticity of tourism demand.
→ Solution
Initial income (Y) = 4000
New income = 5000
Initial quantity demand (Qd) = 10 units
New quantity demand = 40 units
Change in income (ΔY) = 5000 – 4000
= 1000
Change in quantity demand (ΔQd) = 40 – 10
= 30
Using formula,
Ey = (ΔQd / ΔY) * (Y / Qd)
= (30 / 1000) * (4000 / 10)
= 12
Since, 12 > 0, it is positive income elasticity, which indicates positive relation between income and demand.
The income elasticity of tourism demand is 12. This indicates that tourism demand is highly sensitive to changes in income. - Describe the impact of tourism and leisure on national economy.
→
Solution of Year 2018
- State the scope of tourism economics.
→ - Write any two different between scarce and free resources in tourism.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 5 (Please refer back to that year) - List out any four industries the comprises tourism industry.
→ Any four industries the comprises tourism industry are:
i. Accommodation Industry: Includes hotels, resorts, vacation rentals, and other lodging services.
ii. Transportation Industry: includes airlines, cruise lines, car rentals, railways, and other modes of transport that facilitate travel.
iii. Food and Beverage Industry: Consists of restaurants, cafes, bars, catering services, and other food service providers
iv. Attractions and Entertainment Industry: includes theme parks, museums, cultural sites, recreational facilities, and entertainment venues that attract and engage tourists. - What is demand curve?
→ A demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers at various price levels, assuming all other factors remain constant.
It typically slopes downward from left to right, indicating that as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa. - Write any four feature of monopoly.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 10 (Please refer back to that year) - Draw the diagram showing TC, TFC and TVC.
→ TC = TFC + TVC
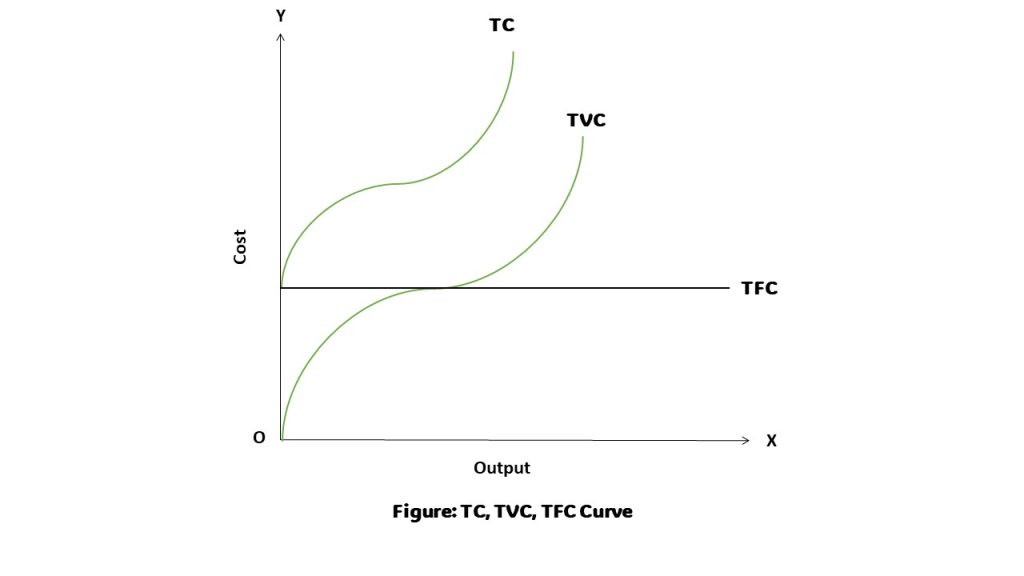
- List out the any four determinants of leisure and tourism.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 7 (Please refer back to that year) - Write down the conditions of price discrimination.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 8 (Please refer back to that year) - What is tourism income multiplier?
→ The tourism income multiplier refers to the effect that spending by tourists has on the local economy, where the initial expenditure generates additional economic activity and income. - List out the factors which cause shift in tourism supply curve.
→ The factors which cause shift in tourism supply curve are:
i. changes in price of the commodity
ii. changes in government policies and regulations
iii. due to technological advancements
iv. occurrence of natural disasters or environmental changes
v. due to infrastructure development - Explain the challenges of development for tourism industry in the Nepalese economy.
→ - Discuss the types of variables influencing tourism demand.
→ - Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative forecasting tourism demand. Briefly explain the importance of tourism demand forecasting.
→ - Define supply function of tourism product. What are the challenges for the supply of tourism product?
→ - How are the price and output determine under perfect competition? Discuss.
→ - Explain how the tourism sectors affect employment, rate of inflation and economic growth?
→ - A) Discuss various degree of price elasticity of demand.
→
B) If the price of the product A increase from 400 to 500.As a results the quantity demand of product B decrease from 10 kg to 5 kg then calculate the cross elasticity of demand. Analyze the results and what recommendations do you provide for pricing decision.
→ Solution
Initial price of the product A (P1 ) = Rs 400
New price of product A (P2) = 500
Initial quantity demand of product B (Q1) = 10 units
New quantity demand of product B (Q2)= 5 units
First, we need to calculate:
Change in price of product A (ΔPA) = P2 – P1
= 500 – 400
= 100
Change in quantity demand of product B (ΔQB) = Q2 – Q1
= 5 – 10
= -5
Next, using formula,
EAB = (ΔQB / ΔPA) * (P1 / Q1)
= (-5 / 100) * (400 / 10)
= -2
Since, the coefficient of cross elasticity of demand between A and B are negative.
The cross elasticity of demand is −2.0, which means that product B is a complementary good to product A. As the price of product A increases, the quantity demanded for product B decreases significantly. - Explain how the private investment and public investment appraised? What are the major differences appraising investment in private and public sector?
→
Solution of Year 2019
- Write any two difference between free and scarce resource.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 5 (Please refer back to that year) - What is GDP?
→ Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period, typically measured annually or quarterly.
It serves as a broad indicator of a country’s economic activity and overall economic health. GDP can be calculated using three approaches: the production (or output) approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach.
(OR)
GDP is a one of the macroeconomic indicator that can be used to measure both a nation’s total income and the total production of goods and services within its economy. - List out any four characteristics of tourism products.
→ Any four characteristics of tourism products are:
i. Intangible: You can’t see or touch tourism products before you purchase them, like a hotel stay or a tour.
ii. Inseparable: The service is delivered and consumed at the same time, like enjoying a guided tour as it’s happening.
iii. Highly Perishable: Tourism products can’t be stored or saved for later; an unsold hotel room is lost revenue.
iv. Variable: The quality of the experience can vary depending on who provides it and when.
v. Customizable: Each tourism experience is unique and can be altered to individual preferences.
vi. Seasonal: Demand for tourism often changes with the seasons or specific events.
Others: Unstable demand, Composite product - What are the determinants of leisure and tourism?
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 7 (Please refer back to that year) - Distinguish between total fixed cost and total variable cost.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 6 (Please refer back to that year) - List out any four factors that cause shifts in tourism demand curve.
→ Any four factors that cause shifts in tourism demand curve are:
i. income
ii. taste and preference
iii. cost of complementary goods
iv. price
v. exchange rates
vi. trade openness
vii. population
viii. attractiveness - Write any four features of perfect competition.
→ Any four features of perfect competition are:
i. Large Number of Sellers and Buyers: The market consists of many buyers and sellers, so no single buyer or seller can influence the market price.
ii. Homogeneous Product: All firms offer identical products, meaning there is no differentiation, and consumers view all products as perfect substitutes.
iii. Free Entry and Exit: Firms can freely enter or exit the market without any barriers, allowing for competition to remain robust and efficient.
iv. No Government Interference: The market operates without government intervention, allowing supply and demand to determine prices naturally.
v. Absence of collusion and independent decision making by firms: Firms operate independently and do not collude with each other, ensuring that competition remains fair and prices reflect true market conditions. - State the essence of inflation.
→ The essence of inflation is the general increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over time, which decreases the purchasing power of money.
This means when there is inflation rise, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services than it did previously, affecting consumers’ cost of living and potentially impacting economic stability. - What is meant by price discrimination?
→ When same product is sold at different prices to different consumers, it is called price discrimination.
For example: Price discrimination on the basis of age; if one RumPum noodle cost Rs 20 for adult person and if same noodle cost Rs 10 for child, it can be said as price discrimination. - List out any four principles of investment in tourism industry.
→ Any four principles of investment in tourism industry are:
i. planning
ii. diversification
iii. understanding risk
iv. calculation of average cost
v. good research
vi. watch the fees and cost
vii. implementation of patience - Explain the importance of tourism industry in the economic development of Nepal.
→ - Explain the concept of tourism multiplier.
→ - What are the challenges for the supplying tourism products?
→ - Explain different types of elasticity of demand. When income of the consumer increases from Rs 5000 to Rs 10,000, quantity demanded increases from 500 units to 800 units, find income elasticity of demand and interpret the result.
→ Solution
Initial income (Y1) = 5000
New income (Y2) = 10000
Initial quantity demand (Q1) = 500 units
New quantity demand (Q2) = 800 units
We know,
Change in income (ΔY) = Y2 – Y1
= 10000 – 5000
= 5000
Change in quantity demand (ΔQ) = Q2 – Q1
= 800 – 500
= 300
Using formula,
Ey = (ΔQ / ΔY) * (Y1/ Q1)
= (300 / 5000) * (5000 / 500)
= 3 / 5
= 0.6
The income elasticity of demand is 0.6. This means that for every 1% increase in income, the quantity demanded of the product increases by 0.6%. The elasticity value of less than 1 indicates that the product is a normal good but income inelastic, meaning that demand for this product increases with income but at a lower proportion than the income increase. - How is the price and the Output determined under monopoly market?
→ - How does a private sector appraise investment in tourism sector?
→ - What is tourism demand forecasting? How is tourism demand forecasted by Survey and time series method?
→ - Explain the impact of leisure and tourism on national economy.
→
Solution of Year 2021
- Explain the various degrees of price elasticity of tourism demand. If the income of a tourist increases from Rs. 8,000 to Rs 10,000 the quantity demanded of tourism product increases from 20 units to 40 units. Compute income elasticity of tourism product. [7 + 3]
→ Solution
Initial price(Y1) = 8000
New price (Y2) = 10000
Initial quantity demand (Q1) = 20 units
New quantity demand (Q2) = 40 units
We know,
Change in income (ΔY) = Y2 – Y1
= 10000 – 8000
= 2000
Change in quantity demand (ΔQ) = Q2 – Q1
= 40 – 20
= 20
Using formula,
Ey = (ΔQ / ΔY) * (Y1/ Q1)
= (20 / 2000) * (8000 / 20)
= 4 - What is perfect competition? How are the price and the output determined under it in short run? [2 + 8]
→ - Define tourism demand forecasting. How is tourism demand forecasted by time series model? [2 + 8]
→ - Explain the prospects and challenges of development of tourism industry in the Nepalese economy. [5 + 5]
→ - Explain the impact of leisure and tourist on national economy.
→ - Define supply function of tourism product. What are the challenges for the supply function of tourism products. [3 + 7]
→ - Explain the determinants of leisure and tourism.
→ - Describe the factors affecting travel and tourism’s yields and future.
→
Solution of Year 2022
- State the scope of economics.
→ The scopes of economics includes:
A. Traditional approach: Under the traditional method economics deals with human and their activities. It deals with those activities of man through which s/he tries to satisfy his or her wants. When the first want is satisfied, second wants arises in our mind immediately. We should make good efforts to get resources or means. Therefore, continuous circle of unlimited wants, efforts and satisfaction are known as scope of economics.
B. Modern approach
i. Microeconomics
ii. Macroeconomics - List out any four factors that cause tourism demand curve to shift to the right.
→ Any four factors that cause tourism demand curve to shift to the right. are
a. Increase in the income of the consumers in case of normal goods
b. Decrease in the income of the consumers in case of inferior goods
c. Increase in the price of substitute goods
d. Fall in the price of complementary goods
e. Consumers taste becoming stronger in favor of the good - List out any four attributes of a tourism product.
→ Repeated question from Year 2019, Question No. 3 (Please refer back to that year) - Define cross elasticity of demand.
→ Cross-elasticity of demand is the measure of responsiveness of demand for the commodity to the changes in the price of its substitutes and complementary goods. - Write down any two purposes of tourism demand forecasting.
→ Any two purposes of tourism demand forecasting are:
i. fulfilling objectives of the business
ii. preparing the budget
iii. taking proper management decisions
iv. evaluating performance - What is a supply schedule?
→ Supply schedule is a tabular statement that gives the law of supply, i.e. it gives the different quantity supplied of a commodity at different prices per unit of time.
A hypothetical supply supply schedule of flour is given below in table
| Combination | Price Rs. per kg | Quantity Kg |
|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | 100 |
| B | 10 | 200 |
| C | 15 | 300 |
- Differentiate between leisure and tourism.
→ The difference between leisure and tourism are
| Basis | Leisure | Tourism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leisure is defined as a quality of experience or as free time. | Tourism is the activity of traveling to and staying in destinations away from one’s usual environment for leisure, business, or other purposes. |
| Examples | spending time spent away from business, work, job hunting, domestic chores, and education | Going on a vacation, visiting historical sites, etc. |
| Multiplier effect | Generally has a lower multiplier effect due to the localized nature of spending. | Often has a higher multiplier effect, as tourist spending circulates through the economy, creating additional economic activity. |
| Employment effects | Can create jobs in local service sectors, but often on a smaller scale. | Creates employment opportunities across various sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and retail. |
| Economic Impact | May have less direct economic impact on local businesses. | Often has a significant impact on local economies, including hotels, restaurants, and attractions. |
- List out the characteristics of perfect competition.
→ Repeated question from Year 2019, Question No.7 (Please refer back to that year) - What is employment multiplier?
→ Employment multiplier is the ratio of a change in total employment to the primary employment. Primary employment stands for the employment of the workers in public works like drainage, digging, roads, buildings, etc.
(OR)
The employment multiplier measures the impact of an initial increase in employment within a sector on the overall employment level in the economy, reflecting the subsequent job creation in related sectors and through increased consumer spending. - Identify the factors that affect travel and tourism’s yields and income.
→ The factors that affect travel and tourism’s yields and income are:
i. Demand Levels: Higher tourist demand can lead to increased yields and income through higher prices and occupancy rates.
ii. Seasonality: Seasonal variations in travel can affect yields, with peak seasons often generating higher income compared to off-peak periods.
others (only write any two of them):
iii. Quality of Services: High-quality services and unique experiences can justify higher prices and improve yields.
iv. Market Segmentation: Targeting different market segments with tailored offerings can optimize revenue and increase yields.
v.Competition: The level of competition in a destination can impact pricing power and income potential.
vi. Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the attractiveness of a destination and impact the income from international tourists.
vii. Marketing and Promotion: Effective marketing and promotional strategies can drive higher demand and improve yields.
viii. Infrastructure and Accessibility: Quality infrastructure and ease of access to destinations can influence tourist spending and overall income. - Explain the impact of tourism on national economy.
→ - Examine the relationship among costs, total revenue and profit in the tourism industry.
→ - Explain the level of choices affecting tourism demand.
→ - Describe the time series model of forecasting tourism, demand.
→ - How are the price and the output determined under monopoly?
→ - Examine the interrelationship between tourism and other sectors of the economy.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 15 (Please refer back to that year) - Explain the various degrees of price elasticity of demand. If the income of consumer increases from Rs. 400 to Rs. 500 and the quantity demanded decreases from 10 Kg to 5 kg then calculate the income elasticity of demand. Analyze the result and what recommendation do you provide for pricing decisions?
→ Solution
Initial income (Y1) = 400
New income (Y2) = 500
Initial quantity demand (Q1) = 10 units
New quantity demand (Q2) = 5 units
We know,
Change in income (ΔY) = Y2 – Y1
= 500 – 400
= 100
Change in quantity demand (ΔQ) = Q2 – Q1
= 5 – 10
= -5
Using formula,
Ey = (ΔQ / ΔY) * (Y1/ Q1)
= (-5 / 100) * (400 / 10)
= -2
Analysis and Recommendations
Result Interpretation: The income elasticity of demand is −2. This negative value indicates that the good is an inferior good, meaning that as income increases, the quantity demanded decreases. The magnitude (2) shows that the demand is elastic with respect to income, implying that the percentage change in quantity demanded is proportionally greater than the percentage change in income.
Pricing Recommendations: For inferior goods with high negative income elasticity, consider that as consumer incomes rise, demand for the product will decrease.
Pricing strategies might include:- Cost Leadership: Keep prices low to attract budget-conscious consumers who might still purchase the good despite rising incomes.
- Diversification: Explore introducing complementary or premium products to capture higher-income consumers who may replace the inferior good with more desirable alternatives.
- Marketing Strategies: Emphasize value for money or functional benefits of the product to maintain demand even as incomes rise.
- Explain the challenges for the development of tourism in Nepal.
→
Solution of Year 2023
- What is mixed economy.
→ Mixed economy is the system that combines aspects of both capitalism and planned.
A mixed economic system protects private property and allows a level of economic freedom in the use of capital, but also allows for governments to interfere in economic activities in order to achieve social aims. - Macroeconomics is also called income and employment theory. Why?
→ Macroeconomics is also called income and employment theory because it focuses on the broad factors that influence a nation’s overall income levels and employment rates. It examines how aggregate income is generated and distributed across the economy and how employment levels are affected by various economic policies, market conditions, and other factors. This branch of economics studies the total output of goods and services, overall employment, inflation, and national income, focusing to understand and manage economic growth and stability. - List out any four examples of tourism products.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 3 (Please refer back to that year) - State the condition for shortage and surplus in market.
→ Here are the conditions for shortage and surplus in a market:
For Shortage
Condition: Occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price.
Cause: Typically results from a price that is set below the equilibrium price, leading to higher demand than the available supply.
For Surplus
Condition: Occurs when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at a given price.
Cause: Typically results from a price that is set above the equilibrium price, leading to lower demand compared to the available supply. - Define opportunity cost.
→ Opportunity cost is what you give up or the benefits you miss out on when choosing one option over another.
For example: If you spend an evening working on a project instead of going out with friends, the opportunity cost is the enjoyment and social experience you miss out on with your friends. - List out any four determinants leisure and tourism.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 7 (Please refer back to that year) - What is tourism demand function?
→ The tourism demand function is a mathematical representation that describes how the quantity of tourism services demanded by consumers varies with changes in various factors, such as prices, income, and other influencing variables.
i.e. Dij = P, E, T, Y, RP, QF
where,
i = Original Place or origin
j = Destination Place
D = Demand of a tourism product
P = Price of the commodity
E = Exchange Rate
T = Transportation
Y = Income Level
RP = Relative price of the commodity
QF = Qualitative factor like mood - What is tourism employment multiplier?
→ Repeated question from Year 2022, Question No. 9 (Please refer back to that year) - What are the conditions for price discrimination?
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 8 (Please refer back to that year) - Write any four causes of inflation.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 9(Please refer back to that year) - What are the challenges for the development of tourism industry in Nepal? Explain.
→ - Explain the interrelationship between tourism and other sectors of the economy.
→ Repeated question from Year 2017, Question No. 15 (Please refer back to that year) - Explain the significance of tourism demand forecasting in taking decision in tourism business.
→ - Show the relationship between total fixed cost (TFC), total variable cost (TVC), total cost (TC), total revenue (TR) and profit.
→ - How does tourism sector affect gross domestic product (GDP), exchange rate and balance of payment? Explain.
→ - How does a private sector appraise investment in tourism sector?
→ - Explain different degrees of income elasticity of demand. Quantity demanded of a commodity decreases from 250 kg to 150 kg due to the increases in price of the commodity from Rs 500 to Rs 600. Find price elasticity of demand and interpret the result.
→ Solution
Original demand (Q1) = 250 kg
Demand after change in price (Q2) = 150 kg
Original price (P1) = Rs 500
Changed price (P2) = Rs 600
Differences in demand (ΔQ) = Q2 – Q1
= 150 – 250
= -100
Differences in price(ΔP) = P2 – P1
= 600 – 500
= 100
Using formula,
= (ΔQ / ΔP) * (P1 / Q1)
= (-100 / 100) * (500 / 250)
= -2
The price elasticity of demand is −2. This negative value indicates that the demand is elastic with respect to price changes. Specifically, a 1% increase in price leads to a 2% decrease in quantity demanded. - Define monopoly. How are the prices and the output determined under it?
→
Practice Question




